Direct interactions between the Paf1 complex and a cleavage and polyadenylation factor are revealed by dissociation of Paf1 from RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 18469135
- PMCID: PMC2446681
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00434-07
Direct interactions between the Paf1 complex and a cleavage and polyadenylation factor are revealed by dissociation of Paf1 from RNA polymerase II
Abstract
The Paf1 complex (Paf1, Ctr9, Cdc73, Rtf1, and Leo1) is normally associated with RNA polymerase II (Pol II) throughout the transcription cycle. However, the loss of either Rtf1 or Cdc73 results in the detachment of the Paf1 complex from Pol II and the chromatin form of actively transcribed genes. Using functionally tagged forms of the Paf1 complex factors, we have determined that, except for the more loosely associated Rtf1, the remaining components stay stably associated with one another in an RNase-resistant complex after dissociation from Pol II and chromatin. The loss of Paf1, Ctr9, or to a lesser extent Cdc73 or Rtf1 results in reduced levels of serine 2 phosphorylation of the Pol II C-terminal domain and in increased read through of the MAK21 polyadenylation site. We found that the cleavage and polyadenylation factor Cft1 requires the Pol II-associated form of the Paf1 complex for full levels of interaction with the serine 5-phosphorylated form of Pol II. When the Paf1 complex is dissociated from Pol II, a direct interaction between Cft1 and the Paf1 complex can be detected. These results are consistent with the Paf1 complex providing a point of contact for recruitment of 3'-end processing factors at an early point in the transcription cycle. The lack of this connection helps to explain the defects in 3'-end formation observed in the absence of Paf1.
Figures


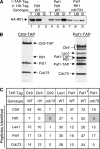
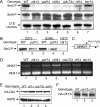
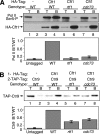

Similar articles
-
Ctr9, Rtf1, and Leo1 are components of the Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):1971-80. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.1971-1980.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884586 Free PMC article.
-
The Paf1 complex has functions independent of actively transcribing RNA polymerase II.Mol Cell. 2004 May 21;14(4):447-56. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00257-6. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15149594
-
Separation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1 complex from RNA polymerase II results in changes in its subnuclear localization.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Jan;4(1):209-20. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.1.209-220.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 15643076 Free PMC article.
-
The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May-Jun;1799(5-6):379-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20060942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyadenylation: a tail of two complexes.Curr Biol. 2002 Dec 23;12(24):R855-7. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01353-2. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12498707 Review.
Cited by
-
The spt5 C-terminal region recruits yeast 3' RNA cleavage factor I.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;32(7):1321-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06310-11. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22290438 Free PMC article.
-
Paf1 restricts Gcn4 occupancy and antisense transcription at the ARG1 promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;32(6):1150-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06262-11. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22252319 Free PMC article.
-
The Paf1 Complex: A Keystone of Nuclear Regulation Operating at the Interface of Transcription and Chromatin.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166979. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166979. Epub 2021 Apr 1. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33811920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tumor suppressor Cdc73 functionally associates with CPSF and CstF 3' mRNA processing factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 20;106(3):755-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812023106. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19136632 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple direct and indirect roles of Paf1C in elongation, splicing, and histone post-translational modifications.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 25:2024.04.25.591159. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.25.591159. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Sep 24;43(9):114730. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114730. PMID: 38712269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ahn, S. H., M. Kim, and S. Buratowski. 2004. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol. Cell 1367-76. - PubMed
-
- Bentley, D. L. 2005. Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of pre-mRNA processing factors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17251-256. - PubMed
-
- Betz, J. L., M. Chang, T. M. Washburn, S. E. Porter, C. L. Mueller, and J. A. Jaehning. 2002. Phenotypic analysis of Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex mutations reveals connections to cell cycle regulation, protein synthesis, and lipid and nucleic acid metabolism. Mol. Genet. Genomics 268272-285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

