Maximizing the treatment of overactive bladder in the elderly
- PMID: 18470275
- PMCID: PMC2312344
Maximizing the treatment of overactive bladder in the elderly
Abstract
Overactive bladder syndrome affects millions of elderly people in the United States and is equally prevalent in men and women. Its impact on quality of life can be devastating, especially to elderly patients with other medical comorbidities. In order to maximize care, health care providers must be able to make the correct diagnosis and have a working knowledge of available therapies. Data exist supporting the efficacy and safety of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies.
Keywords: Antimuscarinic agents; Behavioral therapy; Elderly; Incontinence; Overactive bladder syndrome.
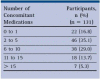
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overactive bladder: treatment options in primary care medicine.J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2007 Sep;107(9):379-85. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2007. PMID: 17908830 Review.
-
Treatments for overactive bladder: focus on pharmacotherapy.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2012 Nov;34(11):1092-1101. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)35440-8. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2012. PMID: 23231848
-
Medical Treatment of Overactive Bladder.Urol Clin North Am. 2022 May;49(2):249-261. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2021.12.005. Urol Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 35428431 Review.
-
Antimuscarinic drug therapy for overactive bladder syndrome in the elderly - are the concerns justified?Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019 May;20(7):813-820. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1574749. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30724647 Review.
-
The safety and efficacy of tolterodine extended release in the treatment of overactive bladder in the elderly.Clin Interv Aging. 2009;4:191-6. doi: 10.2147/cia.s4233. Epub 2009 May 14. Clin Interv Aging. 2009. PMID: 19503781 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overactive bladder in an integrated delivery system: a longitudinal cohort study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 May 20;20(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05315-1. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 32434511 Free PMC article.
-
Use of onabotulinumtoxinA for overactive bladder with concomitant warfarin.Consult Pharm. 2014 Jul;29(7):480-6. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2014.480. Consult Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25203108 Free PMC article.
-
The role of prescription drugs in female overactive bladder syndrome-A population-wide cohort study.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2020 Feb;29(2):189-198. doi: 10.1002/pds.4920. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 31808271 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cumulative anticholinergic burden and falls and fractures in patients with overactive bladder: US-based retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2019 May 5;9(5):e026391. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026391. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31061036 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse events and treatment discontinuations of antimuscarinics for the treatment of overactive bladder in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2017 Mar-Apr;69:77-96. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2017. PMID: 27889591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Magnus F, et al. The standardization of terminology in lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardization Sub-Committee of the International Continence Society. Urology. 2003;61:37–49. - PubMed
-
- Milsom I, Abrams P, Cardozo L, et al. How wide-spread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population-based prevalence study. BJU Int. 2001;87:760–766. - PubMed
-
- Abrams P, Kelleher CJ, Kerr LA, Rogers RG. Overactive bladder significantly affects quality of life. Am J Manag Care. 2000;6(11 suppl):S580–S590. - PubMed
-
- Stewart WF, Van Rooyen JB, Cundiff GW, et al. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J Urol. 1999;44:56–66. - PubMed
-
- Hobbs F, Stoops N. Demographic Trends in the 20th Century. Washington, DC: US Bureau of the Census; 2002. Publication CENSR-4.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
