Structural and functional alterations in the rat lung following whole thoracic irradiation with moderate doses: injury and recovery
- PMID: 18470747
- PMCID: PMC2435093
- DOI: 10.1080/09553000802078396
Structural and functional alterations in the rat lung following whole thoracic irradiation with moderate doses: injury and recovery
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize structural and functional injuries following a single dose of whole-thorax irradiation that might be survivable after a nuclear attack/accident.
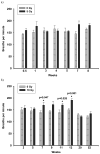
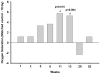
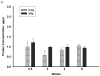
Methods: Rats were exposed to 5 or 10 Gy of X-rays to the whole thorax with other organs shielded. Non-invasive measurements of breathing rate and arterial oxygen saturation, and invasive evaluations of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, (for total protein, Clara cell secretory protein), vascular reactivity and histology were conducted for at least 6 time points up to 52 weeks after irradiation.
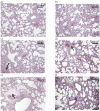
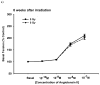
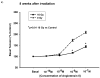
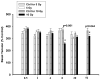
Results: Irradiation with 10 Gy resulted in increased breathing rate, a reduction in oxygen saturation, an increase in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid protein and attenuation of vascular reactivity between 4-12 weeks after irradiation. These changes were not observed with the lower dose of 5 Gy. Histological examination revealed perivascular edema at 4-8 weeks after exposure to both doses, and mild fibrosis beyond 20 weeks after 10 Gy.
Conclusions: Single-dose exposure of rat thorax to 10 but not 5 Gy X-irradiation resulted in a decrease in oxygen uptake and vasoreactivity and an increase in respiratory rate, which paralleled early pulmonary vascular pathology. Vascular edema resolved and was replaced by mild fibrosis beyond 20 weeks after exposure, while lung function recovered.
Figures



References
-
- Arsalane K, Broeckaert F, Knoops B, Wiedig M, Toubeau G, Bernard A. Clara cell specific protein (CC16) expression after acute lung inflammation induced by intratracheal lipopolysaccharide administration. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2000;161:1624–1630. - PubMed
-
- Baughmann RP, Sparkman BK, Lower EE. Six-minute walk test and health status assessment in sarcoidosis. Chest. 2007;132:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Broeckaert F, Clippe A, Knoops B, Hermans C, Bernard A. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2000;923:68–77. - PubMed
-
- Canzian M, Soeiro A, Taga MF, Farhat C, Barbas CSV, Capelozzi VL. Semiquantitative assessment of surgical lung biopsy: predictive value and impact on survival of patients with diffuse pulmonary infiltrate. Clinics. 2007;62:23–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
