Long-term results of the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma with cladribine (2-CDA) alone (95-80-53) or 2-CDA and rituximab (N0189) in the North Central Cancer Treatment Group
- PMID: 18470909
- PMCID: PMC3465670
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23537
Long-term results of the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma with cladribine (2-CDA) alone (95-80-53) or 2-CDA and rituximab (N0189) in the North Central Cancer Treatment Group
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to test cladribine (2-CDA) alone and in combination with rituximab in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Methods: Patients with MCL were treated on 2 sequential trials. In Trial 95-80-53, patients received 2-CDA as initial therapy or at relapse. In Trial N0189, patients received combination 2-CDA and rituximab as initial therapy. In both trials, 2-CDA was administered at a dose of 5 mg/m2 intravenously on Days 1 through 5 every 4 weeks for 2 to 6 cycles, depending on response. In Trial N0189, rituximab 375 mg/m2 was administered on Day 1 of each cycle.
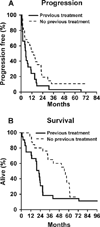
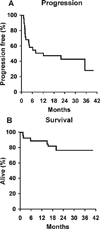
Results: Results were reported for 80 patients. Twenty-six previously untreated patients and 25 patients who had recurrent disease with a median age of 68 years received single-agent 2-CDA. The overall response rate (ORR) was 81% with 42% complete responses (CRs) in the previously untreated group. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 13.6 months (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 7.2-22.1 months), and 81% of patients remained alive at 2 years. The ORR was 46% with a 21% CR rate in the recurrent disease group. The median PFS was 5.4 months (95% CI, 4.6-13.1 months), and 36% of patients remained alive at 2 years. Twenty-nine eligible patients with a median age of 70 years received 2-CDA plus rituximab. The ORR was 66% (19 of 29 patient), and the CR rate was 52% (15 of 29 patients). The median duration of response for patients who achieved a CR had not been reached at the time of the current report, and only 3 of the patients who achieved a CR developed recurrent disease at a median follow-up of 21.5 months.
Conclusions: 2-CDA had substantial single-agent activity in both recurrent and untreated MCL, and the results indicated that it may be administered safely to elderly patients. The addition of rituximab to 2-CDA may increase the duration of response.
(Copyright) 2008 American Cancer Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase I trial of rituximab, cladribine, and temsirolimus (RCT) for initial therapy of mantle cell lymphoma.Ann Oncol. 2014 Oct;25(10):2020-2024. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu273. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25057177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reduced-dose cladribine (2-CdA) plus mitoxantrone is effective in the treatment of mantle-cell and low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Eur J Cancer. 2002 Sep;38(13):1739-46. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00143-0. Eur J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12175690 Clinical Trial.
-
Cladribine plus rituximab is an effective therapy for newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2011 Aug;52(8):1488-94. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.575489. Epub 2011 May 31. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011. PMID: 21623691
-
The epigenetics of mantle cell lymphoma.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2007 Oct;8(5):375-81. doi: 10.1007/s11864-007-0047-8. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2007. PMID: 18214689 Review.
-
Immunotherapy with rituximab following high-dose therapy and autologous stem-cell transplantation for mantle cell lymphoma.Semin Oncol. 2002 Feb;29(1 Suppl 2):56-69. Semin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11842390 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic targets in B- and T-cell lymphomas: latest developments.Ther Adv Hematol. 2023 May 30;14:20406207231173485. doi: 10.1177/20406207231173485. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37273421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase I trial of rituximab, cladribine, and temsirolimus (RCT) for initial therapy of mantle cell lymphoma.Ann Oncol. 2014 Oct;25(10):2020-2024. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu273. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25057177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II trial of the oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in relapsed aggressive lymphoma.Leukemia. 2011 Feb;25(2):341-7. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.226. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21135857 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mantle cell lymphoma: observation to transplantation.Ther Adv Hematol. 2015 Feb;6(1):37-48. doi: 10.1177/2040620714561579. Ther Adv Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25642314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mantle cell lymphoma management trends and novel agents: where are we going?Ther Adv Hematol. 2022 Feb 26;13:20406207221080743. doi: 10.1177/20406207221080743. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Hematol. 2022. PMID: 35237397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zelenetz AD. Mantle cell lymphoma: an update on management. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(suppl 4):iv12–iv14. - PubMed
-
- Witzig TE. Current treatment approaches for mantle-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6409–6414. - PubMed
-
- Bertoni F, Zucca E, Cotter FE. Molecular basis of mantle cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2004;124:130–140. - PubMed
-
- Kurtin PJ. Mantle cell lymphoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 1998;5:376–398. - PubMed
-
- Kurtin PJ, Hobday KS, Ziesmer S, Caron BL. Demonstration of distinct antigenic profiles of small B-cell lymphomas by paraffin section immunohistochemistry. Am J Clin Pathol. 1999;112:319–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA-35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA060276/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-60276/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035272/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35272/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-15083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical