P53, cyclin-dependent kinase and abnormal amplification of centrosomes
- PMID: 18472015
- PMCID: PMC2647860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.04.002
P53, cyclin-dependent kinase and abnormal amplification of centrosomes
Abstract
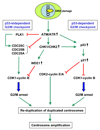
Centrosomes play a critical role in formation of bipolar mitotic spindles, an essential event for accurate chromosome segregation into daughter cells. Numeral abnormalities of centrosomes (centrosome amplification) occur frequently in cancers, and are considered to be the major cause of chromosome instability, which accelerates acquisition of malignant phenotypes during tumor progression. Loss or mutational inactivation of p53 tumor suppressor protein, one of the most common mutations found in cancers, results in a high frequency of centrosome amplification in part via allowing the activation of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2-cyclin E (as well as CDK2-cyclin A) which is a key factor for the initiation of centrosome duplication. In this review, the role of centrosome amplification in tumor progression, and mechanistic view of how centrosomes are amplified in cells through focusing on loss of p53 and aberrant activities of CDK2-cyclins will be discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Bornens M. Centrosome composition and microtubule anchoring mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002;14:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Sattler CA, Sawada N, Sattler GL, Pitot HC. Electron microscopic and time lapse studies of mitosis in cultured rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1988;8:1540–1549. - PubMed
-
- Fukasawa K. Centrosome amplification, chromosome instability and cancer development. Cancer Lett. 2005;230:6–19. - PubMed
-
- Levine DS, Sanchez CA, Rabinovitch PS, Reid BJ. Formation of the tetraploid intermediate is associated with the development of cells with more than four centrioles in the elastase-simian virus 40 tumor antigen transgenic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1991;88:6427–6431. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

