Down-regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1/activin receptor-like kinase 1 pathway gene expression by herbal compound 861 is related to deactivation of LX-2 cells
- PMID: 18473417
- PMCID: PMC2710734
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.2894
Down-regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1/activin receptor-like kinase 1 pathway gene expression by herbal compound 861 is related to deactivation of LX-2 cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of herbal compound 861 (Cpd861) on the transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF beta 1)/activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1, type I receptor) signaling-pathway-related gene expression in the LX-2 cell line, and the inhibitory mechanism of Cpd861 on the activation of LX-2 cells.
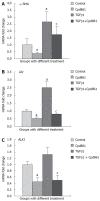
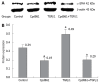
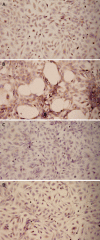
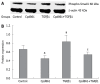
Methods: LX-2 cells were treated with TGF beta 1 (5 ng/mL) Cpd861 (0.1 mg/mL), TGF beta 1 (5 ng/mL) plus Cpd861 (5 ng/mL) for 24 h to investigate the effect of Cpd861 on the TGF beta 1/ALK1 pathway. Real-time PCR was performed to examine the expression of alpha-SMA (alpha-smooth muscle actin), ALK1, Id1 (inhibitor of differentiation 1). Western blotting was carried out to measure the levels of alpha-SMA and phosphorylated Smad1, and immunocytochemical analysis for the expression of alpha-SMA.
Results: In LX-2 cells, TGF beta 1/ALK1-pathway-related gene expression could be stimulated by TGF beta 1, which led to excessive activation of the cells. Cpd861 decreased the activation of LX-2 cells by reducing the expression of alpha-SMA mRNA and protein expression. This effect was related to inhibition of the above TGF beta 1/ALK1-pathway-related expression of genes such as Id1 and ALK1, and phosphorylation of Smad1 in LX-2 cells, even with TGF beta 1 co-treatment for 24 h.
Conclusion: Cpd861 can restrain the activation of LX-2 cells by inhibiting the TGF beta 1/ALK1/Smad1 pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Herbal compound 861 prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad/SnoN pathway in bile duct-ligated rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Feb 5;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2119-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29402324 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β stimulates Smad1/5 signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts of the newborn mouse through ALK1.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):L615-L627. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00079.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28642261 Free PMC article.
-
ALK1 opposes ALK5/Smad3 signaling and expression of extracellular matrix components in human chondrocytes.J Bone Miner Res. 2008 Jun;23(6):896-906. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.080209. J Bone Miner Res. 2008. PMID: 18333754
-
ALK1-Smad1/5 signaling pathway in fibrosis development: friend or foe?Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Dec;24(6):523-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 24055043 Review.
-
ALK1 as an emerging target for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer.Blood. 2011 Jun 30;117(26):6999-7006. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-330142. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21467543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective and Anti-fibrotic Agents: It's Time to Take the Next Step.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Jan 7;6:303. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00303. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26779021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β1 improves mucosal IgA dysfunction and dysbiosis following intestinal ischaemia-reperfusion in mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Jun;20(6):1014-23. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12789. Epub 2016 Jan 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26820382 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the human Activin-A receptor type II-like kinase 1 (ACVRL1) promoter and its regulation by Sp1.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Jun 29;11:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-51. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20587022 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of BMP9 in liver fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 11;15(11):20656-67. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120656. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25393508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin suppresses proliferation and differentiation induced by BMP9 via AMPK signaling in human fetal lung fibroblast-1.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:984730. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984730. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2247–2250. - PubMed
-
- Iredale JP. Hepatic stellate cell behavior during resolution of liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:427–436. - PubMed
-
- Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K, Dooley S. Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d793–d807. - PubMed
-
- Parsons CJ, Takashima M, Rippe RA. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22 Suppl 1:S79–S84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

