Motion estimation for cardiac emission tomography by optical flow methods
- PMID: 18475004
- PMCID: PMC2424264
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/53/11/016
Motion estimation for cardiac emission tomography by optical flow methods
Abstract
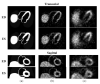
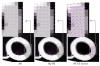
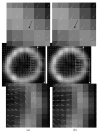
This paper describes a new method for estimating the 3D, non-rigid object motion in a time sequence of images. The method is a generalization of a standard optical flow algorithm that is incorporated into a successive quadratic approximation framework. The method was evaluated for gated cardiac emission tomography using images obtained from a mathematical, 4D phantom and a physical, dynamic phantom. The results showed that the proposed method offers improved motion estimation accuracy relative to the standard optical flow method. Convergence of the proposed algorithm was evidenced with a monotonically decreasing objective function value with iteration. Practical application of the motion estimation method in cardiac emission tomography includes quantitative myocardial motion estimation and 4D, motion-compensated image reconstruction.
Figures





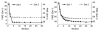

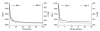
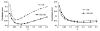

References
-
- Alvarez L, Weickert J, Sanchez J. Reliable estimation of dense optical flow fields with large displacements. Int. J. Comp. Vis. 2000;39:41–56.
-
- Black MJ, Anandan P. The robust estimation of multiple motions: parametric and piecewise-smooth flow fields. Comput. Vis. Image Understand. 1996;63:75–104.
-
- Brankov JG, Yang Y, Wernick MN. Spatiotemporal processing of gated cardiac SPECT images using deformable mesh modeling. Med. Phys. 2005;32:2839–49. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham GS, Hanson KM, Battle XL. Three-dimensional reconstructions from low-count SPECT data using deformable models. Opt. Exp. 1998;2:227–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
