Simple detection of large InDeLS by DHPLC: the ACE gene as a model
- PMID: 18475319
- PMCID: PMC2358980
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/562183
Simple detection of large InDeLS by DHPLC: the ACE gene as a model
Abstract
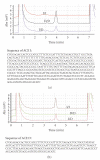
Insertion-deletion polymorphism (InDeL) is the second most frequent type of genetic variation in the human genome. For the detection of large InDeLs, researchers usually resort to either PCR gel analysis or RFLP, but these are time consuming and dependent on human interpretation. Therefore, a more efficient method for genotyping this kind of genetic variation is needed. In this report, we describe a method that can detect large InDeLs by DHPLC (denaturating high-performance liquid chromatography) using the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) gene I/D polymorphism as a model. The InDeL targeted in this study is characterized by a 288 bp Alu element insertion (I). We used DHPLC at nondenaturating conditions to analyze the PCR product with a flow through the chromatographic column under two different gradients based on the differences between D and I sequences. The analysis described is quick and easy, making this technique a suitable and efficient means for DHPLC users to screen InDeLs in genetic epidemiological studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA from buccal swab is suitable for rapid genotyping of angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Apr 20;431:125-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.12.041. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24406276
-
The I/D polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene and asthma risk: a meta-analysis.Allergy. 2011 Feb;66(2):197-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02438.x. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Allergy. 2011. PMID: 20880211
-
Real-time PCR for rapid genotyping of angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism.Clin Biochem. 2001 Nov;34(8):661-6. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(01)00281-8. Clin Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11849627
-
Development of a high-resolution melting genotyping assay for the angiotensin I converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and establishment of genotype-specific reference intervals in a Danish population.Ann Clin Biochem. 2015 Jan;52(Pt 1):105-12. doi: 10.1177/0004563214529261. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Ann Clin Biochem. 2015. PMID: 24696153
-
Associations between the angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and susceptibility to sarcoidosis: A meta-analysis.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015 Mar;16(1):219-26. doi: 10.1177/1470320313489059. Epub 2013 May 15. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015. PMID: 23676252 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism genotyping error: the cause and a possible solution to the problem.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jul;40(7):4459-63. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2537-z. Epub 2013 May 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23657592
-
Development of Novel High-Resolution Melting-Based Assays for Genotyping Two Alu Insertion Polymorphisms (FXIIIB and PV92).Mol Biotechnol. 2016 Mar;58(3):197-201. doi: 10.1007/s12033-016-9915-4. Mol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26843017
References
-
- Ball EV, Stenson PD, Abeysinghe SS, Krawczak M, Cooper DN, Chuzhanova NA. Microdeletions and microinsertions causing human genetic disease: common mechanisms of mutagenesis and the role of local DNA sequence complexity. Human Mutation. 2005;26(3):205–213. - PubMed
-
- Cambien F, Poirier O, Lecerf L, et al. Deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Nature. 1992;359(6396):641–644. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt S, van Hooft IM, Grobbee DE, Ganten D, Ritz E. Polymorphism of the angiotensin I converting enzyme gene is apparently not related to high blood pressure: dutch hypertension and offspring study. Journal of Hypertension. 1993;11(4):345–348. - PubMed
-
- Lindpaintner K, Pfeffer MA, Kreutz R, et al. A prospective evaluation of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme gene polymorphism and the risk of ischemic heart disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1995;332(11):706–711. - PubMed
-
- Álvarez R, González P, Batalla A, et al. Association between the NOS3 (-786 T/C) and the ACE (I/D) DNA genotypes and early coronary artery disease. Nitric Oxide. 2001;5(4):343–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

