TRAIL recombinant adenovirus triggers robust apoptosis in multidrug-resistant HL-60/Vinc cells preferentially through death receptor DR5
- PMID: 18476767
- PMCID: PMC2733364
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2008.001
TRAIL recombinant adenovirus triggers robust apoptosis in multidrug-resistant HL-60/Vinc cells preferentially through death receptor DR5
Abstract
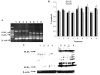
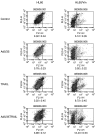
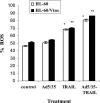
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising cancer therapeutic because of its highly selective apoptosis-inducing action on neoplastic versus normal cells. However, some cancer cells express resistance to recombinant soluble TRAIL. To overcome this problem, we used a TRAIL adenovirus (Ad5/35-TRAIL) to induce apoptosis in a drug-sensitive and multidrug-resistant variant of HL-60 leukemia cells and determined the molecular mechanisms of Ad5/35-TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Ad5/35-TRAIL did not induce apoptosis in normal human lymphocytes, but caused massive apoptosis in acute myelocytic leukemia cells. It triggered more efficient apoptosis in drug-resistant HL-60/Vinc cells than in HL-60 cells. Treating the cells with anti-DR4 and anti-DR5 neutralizing antibodies (particularly anti-DR5) reduced, whereas anti-DcR1 antibody enhanced, the apoptosis triggered by Ad5/35-TRAIL. Whereas Ad5/35-TRAIL induced apoptosis in both cell lines through activation of caspase-3 and caspase-10, known to link the cell death receptor pathway to the mitochondrial pathway, it triggered increased mitochondrial membrane potential change (m) only in HL-60/Vinc cells. Ad5/35-TRAIL also increased the production of reactive oxygen species, which play an important role in apoptosis. Therefore, using Ad5/35-TRAIL may be an effective therapeutic strategy for eliminating TRAIL-resistant malignant cells and these studies may provide clues to treat and eradicate acute myelocytic leukemias.
Figures
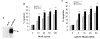
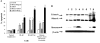
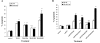

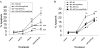
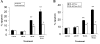
References
-
- Abedini M.R. Qiu Q. Yan X. Tsang B.K. Possible role of FLICE-like inhibitory protein (FLIP) in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Oncogene. 2004;23:6997–7004. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A. Pai R.C. Fong S. Leung S. Lawrence D.A. Marsters S.A. Blackie C. Chang L. McMurtrey A.E. Hebert A. Deforge L. Koumenis I.L. Lewis D. Harris L. Bussiere J. Koeppen H. Shahrokh Z. Schwall R.H. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J. Clin. Invest. 1999;104:155–162. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balamotis M.A. Huang K. Mitani K. Efficient delivery and stable gene expression in a hematopoietic cell line using a chimeric serotype 35 fiber pseudotyped helper-dependent adenoviral vector. Virology. 2004;324:229–237. - PubMed
-
- Bedi A. Zehnbauer B.A. Barber J.P. Sharkis S.J. Jones R.J. Inhibition of apoptosis by BCR-ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1994;83:2038–2044. - PubMed
-
- Bedi A. Barber J.P. Bedi G.C. El-Deiry W.S. Sidransky D. Vala M.S. Akhtar A.J. Hilton J. Jones R.J. BCR-ABL mediated inhibition of apoptosis with delay of G2/M transition after DNA damage: A mechanism of resistance to multiple anticancer agents. Blood. 1995;86:1148–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

