Emerging role for AS160/TBC1D4 and TBC1D1 in the regulation of GLUT4 traffic
- PMID: 18477703
- PMCID: PMC2493596
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90331.2008
Emerging role for AS160/TBC1D4 and TBC1D1 in the regulation of GLUT4 traffic
Abstract
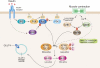
Vesicular traffic of the glucose transporter GLUT4 occurs in response to insulin, muscle contraction, and metabolic stimuli that lead to changes in the energy status of the cell. These stimuli are associated with linked kinase cascades that lead to changes in glucose uptake that meet the energy challenges imposed on the highly regulated cell types in insulin-responsive tissues. The need to mechanistically link these kinase-associated stimuli to identifiable intermediates in vesicular traffic has long been known but has been difficult to fulfill. The Rab-GTPase-activating proteins AS160 and TBC1D1 have now emerged as strong candidates to fill this void. Here we review the initial discovery of these proteins as phosphorylated substrates for Akt and the more recent emerging data that indicate that these proteins are substrates for additional kinases that are downstream of contraction and energy status signaling. The mechanism of coupling these phosphorylated proteins to vesicle traffic appears to be dependent on linking to small GTPase of the Rab family. We examine the current state of a hypothesis that suggests that phosphorylation of the Rab-GTPase-activating proteins leads to increased GTP loading of Rab proteins on GLUT4 vesicles and subsequently to increased interaction with Rab effectors that control GLUT4 vesicle translocation.
Figures

References
-
- Alessi DR, Caudwell FB, Andjelkovic M, Hemmings BA, Cohen P. Molecular basis for the substrate specificity of protein kinase B; comparison with MAPKAP kinase-1 and p70 S6 kinase. FEBS Lett 399: 333–338, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Bai L, Wang Y, Fan J, Chen Y, Ji W, Qu A, Xu P, James DE, Xu T. Dissecting multiple steps of GLUT4 trafficking and identifying the sites of insulin action. Cell Metab 5: 47–57, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Barnett SF, Defeo-Jones D, Fu S, Hancock PJ, Haskell KM, Jones RE, Kahana JA, Kral AM, Leander K, Lee LL, Malinowski J, McAvoy EM, Nahas DD, Robinson RG, Huber HE. Identification and characterization of pleckstrin-homology-domain-dependent and isoenzyme-specific Akt inhibitors. Biochem J 385: 399–408, 2005. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouzakri K, Ribaux P, Tomas A, Parnaud G, Rickenbach K, Halban PA. Rab GTPase-activating protein AS160 is a major downstream effector of protein kinase B/Akt signaling in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 57: 1195–1204, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Bruss MD, Arias EB, Lienhard GE, Cartee GD. Increased phosphorylation of Akt substrate of 160 kDa (AS160) in rat skeletal muscle in response to insulin or contractile activity. Diabetes 54: 41–50, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

