Excessive islet NO generation in type 2 diabetic GK rats coincides with abnormal hormone secretion and is counteracted by GLP-1
- PMID: 18478125
- PMCID: PMC2367446
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002165
Excessive islet NO generation in type 2 diabetic GK rats coincides with abnormal hormone secretion and is counteracted by GLP-1
Erratum in
- PLoS ONE. 2008;3(6). doi: 10.1371/annotation/5efa5d3b-2733-4629-9592-f41e0814ca0b
- PLoS ONE. 2008;3(6). doi: 10.1371/annotation/a72da6a5-a71a-4cc9-ae2b-2b95c0ec89b0
- PLoS ONE. 2008;3(6). doi: 10.1371/annotation/bea154a4-93b3-4f1a-9948-acbaae12d256
Abstract
Background: A distinctive feature of type 2 diabetes is inability of insulin-secreting beta-cells to properly respond to elevated glucose eventually leading to beta-cell failure. We have hypothesized that an abnormally increased NO production in the pancreatic islets might be an important factor in the pathogenesis of beta-cell dysfunction.
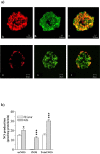
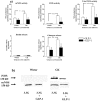
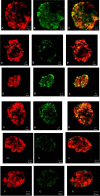
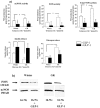
Principal findings: We show now that islets of type 2 spontaneous diabetes in GK rats display excessive NO generation associated with abnormal iNOS expression in insulin and glucagon cells, increased ncNOS activity, impaired glucose-stimulated insulin release, glucagon hypersecretion, and impaired glucose-induced glucagon suppression. Pharmacological blockade of islet NO production by the NOS inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) greatly improved hormone secretion from GK islets suggesting islet NOS activity being an important target to inactivate for amelioration of islet cell function. The incretin hormone GLP-1, which is used in clinical practice suppressed iNOS and ncNOS expression and activity with almost full restoration of insulin release and partial restoration of glucagon release. GLP-1 suppression of iNOS expression was reversed by PKA inhibition but unaffected by the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Injection of glucose plus GLP-1 in the diabetic rats showed that GLP-1 amplified the insulin response but induced a transient increase and then a poor depression of glucagon.
Conclusion: The results suggest that abnormally increased NO production within islet cells is a significant player in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes being counteracted by GLP-1 through PKA-dependent, nonproteasomal mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the GK rat is associated with abnormalities in islet nitric oxide production.Regul Pept. 2008 Nov 29;151(1-3):139-46. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2008.07.002. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Regul Pept. 2008. PMID: 18662725
-
Glucose stimulates the expression and activities of nitric oxide synthases in incubated rat islets: an effect counteracted by GLP-1 through the cyclic AMP/PKA pathway.Cell Tissue Res. 2005 Feb;319(2):221-30. doi: 10.1007/s00441-004-1013-4. Epub 2004 Nov 19. Cell Tissue Res. 2005. PMID: 15558323
-
Chronic blockade of NO synthase paradoxically increases islet NO production and modulates islet hormone release.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Jul;279(1):E95-E107. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2000.279.1.E95. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000. PMID: 10893328
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:377-99. doi: 10.1210/rp.56.1.377. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11237222 Review.
-
The multifaceted potential of glucagon-like peptide-1 as a therapeutic agent.Minerva Endocrinol. 2002 Jun;27(2):79-93. Minerva Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11961501 Review.
Cited by
-
Possible contribution of taurine to distorted glucagon secretion in intra-islet insulin deficiency: a metabolome analysis using a novel α-cell model of insulin-deficient diabetes.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e113254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113254. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25393115 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous extract of Peristrophe bivalvis (L.) Merr. leaf reversed the detrimental effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on blood lipid profile and glucose level.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0308338. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308338. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240961 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Impacts of Sitagliptin on the Pancreas of a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Drug Interactions with Metformin.Biology (Basel). 2019 Dec 25;9(1):6. doi: 10.3390/biology9010006. Biology (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31881657 Free PMC article.
-
The functional impact of G protein-coupled receptor 142 (Gpr142) on pancreatic β-cell in rodent.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Apr;471(4):633-645. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02262-7. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30767071 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of hepatic insulin sensitivity induced by central lipid infusion in rats is mediated by nitric oxide.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 14;4(8):e6649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006649. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19680547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salehi A, Carlberg M, Henningson R, Lundquist I. Islet constitutive nitric oxide synthase: biochemical determination and regulatory function. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:C1634–1641. - PubMed
-
- Salehi A, Ekelund M, Henningsson R, Lundquist I. Total parenteral nutrition modulates hormone release by stimulating expression and activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrine. 2001;16:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Salehi A, Ekelund M, Lundquist I. Total parenteral nutrition-stimulated activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat pancreatic islets is suppressed by glucagon-like peptide-1. Horm Metab Res. 2003;35:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Henningsson R, Alm P, Ekstrom P, Lundquist I. Heme oxygenase and carbon monoxide: regulatory roles in islet hormone release: a biochemical, immunohistochemical, and confocal microscopic study. Diabetes. 1999;48:66–76. - PubMed
-
- Akesson B, Henningsson R, Salehi A, Lundquist I. Islet constitutive nitric oxide synthase and glucose regulation of insulin release in mice. J Endocrinol. 1999;163:39–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

