Subthreshold auditory inputs to extrastriate visual neurons are responsive to parametric changes in stimulus quality: sensory-specific versus non-specific coding
- PMID: 18479671
- PMCID: PMC2645081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.03.086
Subthreshold auditory inputs to extrastriate visual neurons are responsive to parametric changes in stimulus quality: sensory-specific versus non-specific coding
Abstract
A new subthreshold form of multisensory processing has been recently identified that results from the convergence of suprathreshold excitatory inputs from one modality with subthreshold inputs from another. Because of the subthreshold nature of the second modality, descriptive measures of sensory features such as receptive field properties or location are not directly apparent as they are for traditional bimodal neurons. This raises the question of whether or not subthreshold signals actually convey sensory-specific receptive field information as seen in their bimodal counterparts, or if they represent non-specific effects such as arousal. The present experiment addressed this issue in visually-responsive neurons from the cat posterolateral lateral suprasylvian cortex (PLLS). Single-unit electrophysiological techniques were used to record neuronal responses to visual, auditory and combined visual-auditory stimuli while the intensity of stimulation in the subthreshold auditory modality was systematically altered. The results showed that subthreshold multisensory neurons were sensitive to changes in auditory stimulus intensity. These receptive field sensitivities are similar to those observed in bimodal neurons and thereby represent sensory-specific, not arousal-related responses. In addition, these results provide further support for the notion that multisensory processing occurs along a dynamic continuum of neuronal convergence patterns from bimodal to purely sensory-specific.
Figures
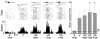


References
-
- Allman BL, Meredith MA. Multisensory processing in ‘unimodal’ neurons: cross-modal subthreshold auditory effects in cat extrastriate visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98:545–549. - PubMed
-
- Barraclough NE, Xiao D, Baker CI, Oram MW, Perrett DI. Integration of visual and auditory information by Superior Temporal Sulcus neurons responsive to the sight of actions. J Cog Neurosci. 2005;17:377–391. - PubMed
-
- Blair RW, Thompson GM. Convergence of multiple sensory inputs onto neurons in the dorsolateral medulla in cats. Neuroscience. 1995;67:721–729. - PubMed
-
- Brugge JF, Merzenich MM. Responses of neurons in auditory cortex of the macacuqe monkey to monaural and binaural stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1973;36:1138–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

