Feasibility of using hyperpolarized [1-13C]lactate as a substrate for in vivo metabolic 13C MRSI studies
- PMID: 18479878
- PMCID: PMC2577896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2008.01.002
Feasibility of using hyperpolarized [1-13C]lactate as a substrate for in vivo metabolic 13C MRSI studies
Abstract
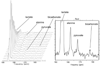
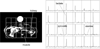
The development of dynamic nuclear polarization in solution has enabled in vivo 13C MR studies at high signal-to-noise ratio following injection of prepolarized 13C substrates. While prior studies have demonstrated the ability to observe metabolism following injection of hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate, the goal of this study was to develop and test a new hyperpolarized agent for investigating in vivo metabolism, [1-13C]lactate. A preparation for prepolarized 13C lactate and the requisite dissolution media were developed to investigate the feasibility for in vivo 13C MRS/MRSI studies following injection of this hyperpolarized agent. This study demonstrated, for the first time, not only the ability to detect hyperpolarized [1-13C]lactate in vivo but also the metabolic products 13C pyruvate, 13C alanine and 13C bicarbonate following injection in normal rats. The use of 13C lactate as a substrate provided the opportunity to study the conversion of lactate to pyruvate in vivo and to detect the secondary conversions to alanine and bicarbonate through pyruvate. This study also demonstrated the potential value of this hyperpolarized agent to investigate in vivo lactate uptake and metabolism in preclinical animal models.
Figures

References
-
- Chen AP, Alberts MJ, Cunningham CH, Kohler SJ, Yen Y, Hurd RE, Tropp J, Bok R, Pauly JM, Nelson SJ, Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB. Hyperpolarized C-13 Spectroscopic Imaging of the TRAMP Mouse at 3T – Initial Experience. Magn Reson Med. In-Press. - PubMed
-
- Kohler SJ, Yen Y, Wolber J, Chen AP, Albers MJ, Bok R, Zhang V, Tropp J, Nelson S, Vigneron DB, Kurhanewicz J, Hurd RE. In vivo 13 carbon metabolic imaging at 3T with hyperpolarized 13C-1-pyruvate. Mag Res Med. 2007;58(1):65–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

