DNA mismatch repair-dependent activation of c-Abl/p73alpha/GADD45alpha-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 18480060
- PMCID: PMC2490771
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M709954200
DNA mismatch repair-dependent activation of c-Abl/p73alpha/GADD45alpha-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
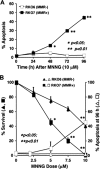
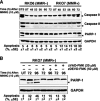
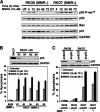
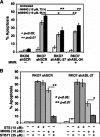
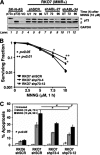
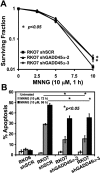
Cells with functional DNA mismatch repair (MMR) stimulate G(2) cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis in response to N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG). MMR-deficient cells fail to detect MNNG-induced DNA damage, resulting in the survival of "mutator" cells. The retrograde (nucleus-to-cytoplasm) signaling that initiates MMR-dependent G(2) arrest and cell death remains undefined. Since MMR-dependent phosphorylation and stabilization of p53 were noted, we investigated its role(s) in G(2) arrest and apoptosis. Loss of p53 function by E6 expression, dominant-negative p53, or stable p53 knockdown failed to prevent MMR-dependent G(2) arrest, apoptosis, or lethality. MMR-dependent c-Abl-mediated p73alpha and GADD45alpha protein up-regulation after MNNG exposure prompted us to examine c-Abl/p73alpha/GADD45alpha signaling in cell death responses. STI571 (Gleevec, a c-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor) and stable c-Abl, p73alpha, and GADD45alpha knockdown prevented MMR-dependent apoptosis. Interestingly, stable p73alpha knockdown blocked MMR-dependent apoptosis, but not G(2) arrest, thereby uncoupling G(2) arrest from lethality. Thus, MMR-dependent intrinsic apoptosis is p53-independent, but stimulated by hMLH1/c-Abl/p73alpha/GADD45alpha retrograde signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MMR/c-Abl-dependent activation of ING2/p73alpha signaling regulates the cell death response to N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine.Exp Cell Res. 2009 Nov 1;315(18):3163-75. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.09.010. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19766113 Free PMC article.
-
Role of c-Abl kinase in DNA mismatch repair-dependent G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest responses.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 1;283(31):21382-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709953200. Epub 2008 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18480061 Free PMC article.
-
MLH1- and ATM-dependent MAPK signaling is activated through c-Abl in response to the alkylator N-methyl-N'-nitro-N'-nitrosoguanidine.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):32021-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701451200. Epub 2007 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17804421
-
Choosing between growth arrest and apoptosis through the retinoblastoma tumour suppressor protein, Abl and p73.Biochem Soc Trans. 2001 Nov;29(Pt 6):666-73. doi: 10.1042/0300-5127:0290666. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. PMID: 11709051 Review.
-
Determination of cell fate by c-Abl activation in the response to DNA damage.Oncogene. 1998 Dec 24;17(25):3309-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202571. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9916993 Review.
Cited by
-
c-Abl inhibits breast cancer tumorigenesis through reactivation of p53-mediated p21 expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):72777-72794. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11909. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626309 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Abl kinase inhibits oncogenic transforming growth factor-beta signaling and tumorigenesis in mammary tumors.FASEB J. 2009 Dec;23(12):4231-43. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-138412. Epub 2009 Aug 18. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19690215 Free PMC article.
-
Low dose IR-induced IGF-1-sCLU expression: a p53-repressed expression cascade that interferes with TGFβ1 signaling to confer a pro-survival bystander effect.Oncogene. 2013 Jan 24;32(4):479-90. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.64. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22391565 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of early Abl kinase activation after ionizing radiation by using a peptide biosensor.Chembiochem. 2012 Mar 19;13(5):665-73. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100763. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Chembiochem. 2012. PMID: 22334513 Free PMC article.
-
Translational potential of GADD45α: biomarker and therapeutic target in age-associated neurodegeneration and longevity.Biogerontology. 2025 Jun 30;26(4):135. doi: 10.1007/s10522-025-10277-0. Biogerontology. 2025. PMID: 40586967 Review.
References
-
- Jiricny, J. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7 335-346 - PubMed
-
- Hawn, M. T., Umar, A., Carethers, J. M., Marra, G., Kunkel, T. A., Boland, C. R., and Koi, M. (1995) Cancer Res. 55 3721-3725 - PubMed
-
- Meyers, M., Hwang, A., Wagner, M. W., and Boothman, D. A. (2004) Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 44 249-264 - PubMed
-
- Fishel, R., Lescoe, M. K., Rao, M. R. S., Copeland, N. G., Jenkins, N. A., Garber, J., Kane, M., and Kolodner, R. (1993) Cell 75 1027-1038 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

