Rapid discovery and optimization of therapeutic antibodies against emerging infectious diseases
- PMID: 18480090
- PMCID: PMC2461042
- DOI: 10.1093/protein/gzn027
Rapid discovery and optimization of therapeutic antibodies against emerging infectious diseases
Abstract
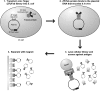
Using a comprehensive set of discovery and optimization tools, antibodies were produced with the ability to neutralize SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection in Vero E6 cells and in animal models. These anti-SARS antibodies were discovered using a novel DNA display method, which can identify new antibodies within days. Once neutralizing antibodies were identified, a comprehensive and effective means of converting the mouse sequences to human frameworks was accomplished using HuFR (human framework reassembly) technology. The best variant (61G4) from this screen showed a 3.5-4-fold improvement in neutralization of SARS-CoV infection in vitro. Finally, using a complete site-saturation mutagenesis methodology focused on the CDR (complementarity determining regions), a single point mutation (51E7) was identified that improved the 80% plaque reduction neutralization of the virus by greater than 8-fold. These discovery and evolution strategies can be applied to any emerging pathogen or toxin where a causative agent is known.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protection of mammalian cells from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection by equine neutralizing antibody.Antivir Ther. 2005;10(5):681-90. Antivir Ther. 2005. PMID: 16152762
-
Development and characterization of a severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus-neutralizing human monoclonal antibody that provides effective immunoprophylaxis in mice.J Infect Dis. 2005 Feb 15;191(4):507-14. doi: 10.1086/427242. Epub 2005 Jan 14. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15655773 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biological characterization of human monoclonal antibodies binding to the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1635-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1635-1644.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650189 Free PMC article.
-
SARS patients-derived human recombinant antibodies to S and M proteins efficiently neutralize SARS-coronavirus infectivity.Biomed Environ Sci. 2005 Dec;18(6):363-74. Biomed Environ Sci. 2005. PMID: 16544518
-
Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody.Nature. 2020 Jul;583(7815):290-295. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2349-y. Epub 2020 May 18. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32422645
Cited by
-
Plasmid Display for Stabilization of Enzymes Inside the Cell to Improve Whole-Cell Biotransformation Efficiency.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jan 10;7:444. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00444. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31998709 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for Targeting SARS CoV-2: Small Molecule Inhibitors-The Current Status.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 18;11:552925. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.552925. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus chemotherapy.Future Virol. 2011 May;6(5):615-631. doi: 10.2217/fvl.11.33. Future Virol. 2011. PMID: 21765859 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

