Distinct roles for IL-13 and IL-4 via IL-13 receptor alpha1 and the type II IL-4 receptor in asthma pathogenesis
- PMID: 18480254
- PMCID: PMC2386078
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0802465105
Distinct roles for IL-13 and IL-4 via IL-13 receptor alpha1 and the type II IL-4 receptor in asthma pathogenesis
Abstract
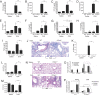
IL-13 and IL-4 are central T helper 2 (Th2) cytokines in the immune system and potent activators of inflammatory responses and fibrosis during Th2 inflammation. Recent studies using Il13ra1(-/-) mice have demonstrated a critical role for IL-13 receptor (IL-13R) alpha1 in allergen-induced airway responses. However, these observations require further attention especially because IL-4 can induce similar lung pathology to IL-13, independent of IL-13, and is still present in the allergic lung. Thus, we hypothesized that IL-13Ralpha1 regulates IL-4-induced responses in the lung. To dissect the role of IL-13Ralpha1 and the type I and II IL-4Rs in experimental asthma, we examined lung pathology induced by allergen, IL-4, and IL-13 challenge in Il13ra1(-/-) mice. We report that IL-13Ralpha1 is essential for baseline IgE production, but Th2 and IgE responses to T cell-dependent antigens are IL-13Ralpha1-independent. Furthermore, we demonstrate that increased airway resistance, mucus, TGF-beta, and eotaxin(s) production, but not cellular infiltration, are critically dependent on IL-13Ralpha1. Surprisingly, our results identify a CCR3- and IL-13Ralpha1-independent pathway for lung eosinophilia. Global expression profiling of lungs from mice stimulated with allergen or IL-4 demonstrated that marker genes of alternatively activated macrophages are differentially regulated by the type I and type II IL-4R. Taken together, our data provide a comprehensive mechanistic analysis of the critical role by which IL-13Ralpha1 mediates allergic lung pathology and highlight unforeseen roles for the type II IL-4R.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: F.D.F. is a consultant for Amgen, Abbott, Plexxikon, CSI, Schering–Plough, Centocor, and Peptimmune and has received research support from Abbott, Amgen, Centocor, and Plexxikon. M.E.R. is a consultant for Merck and Ception Therapeutics.
Figures

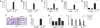
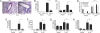

References
-
- Wynn TA. IL-13 effector functions. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:425–456. - PubMed
-
- Elias JA, Lee CG, Zheng T, Shim Y, Zhu Z. Interleukin-13 and leukotrienes: An intersection of pathogenetic schema. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;28:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Mattes J, et al. IL-13 induces airways hyperreactivity independently of the IL-4R alpha chain in the allergic lung. J Immunol. 2001;167:1683–1692. - PubMed
-
- Mentink-Kane MM, Wynn TA. Opposing roles for IL-13 and IL-13 receptor alpha 2 in health and disease. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:191–202. - PubMed
-
- Fichtner-Feigl S, et al. Induction of IL-13 triggers TGF-beta1-dependent tissue fibrosis in chronic 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis. J Immunol. 2007;178:5859–5870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

