Growth/differentiation factor 3 signals through ALK7 and regulates accumulation of adipose tissue and diet-induced obesity
- PMID: 18480259
- PMCID: PMC2438236
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0800272105
Growth/differentiation factor 3 signals through ALK7 and regulates accumulation of adipose tissue and diet-induced obesity
Abstract
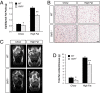
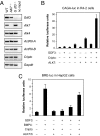
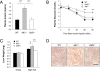
Growth/differentiation factor 3 (GDF3) is highly expressed in adipose tissue, and previous overexpression experiments in mice have suggested that it may act as an adipogenic factor under conditions of high lipid load. GDF3 has been shown to signal via the activin receptor ALK4 during embryogenesis, but functional receptors in adipose tissue are unknown. In this study, we show that Gdf3(-/-) mutant mice accumulate less adipose tissue than WT animals and show partial resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity despite similar food intake. We also demonstrate that GDF3 can signal via the ALK4-homolog ALK7 and the coreceptor Cripto, both of which are expressed in adipose tissue. In agreement with a role for ALK7 in GDF3 signaling in vivo, mutant mice lacking ALK7 also showed reduced fat accumulation and partial resistance to diet-induced obesity. We propose that GDF3 regulates adipose-tissue homeostasis and energy balance under nutrient overload in part by signaling through the ALK7 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin Regulates Lipolysis and Fat Mass by Upregulating Growth/Differentiation Factor 3 in Adipose Tissue Macrophages.Diabetes. 2018 Sep;67(9):1761-1772. doi: 10.2337/db17-1201. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29945891
-
Adipocyte ALK7 links nutrient overload to catecholamine resistance in obesity.Elife. 2014 Aug 25;3:e03245. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03245. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25161195 Free PMC article.
-
Acute regulation of murine adipose tissue lipolysis and insulin resistance by the TGFβ superfamily protein GDF3.Nat Commun. 2025 May 13;16(1):4432. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59673-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40360531 Free PMC article.
-
The GDF3-ALK7 signaling axis in adipose tissue: a possible therapeutic target for obesity and associated diabetes?Endocr J. 2023 Aug 28;70(8):761-770. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ23-0112. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Endocr J. 2023. PMID: 37081691 Review.
-
Regulation of metabolic homeostasis by the TGF-β superfamily receptor ALK7.FEBS J. 2022 Oct;289(19):5776-5797. doi: 10.1111/febs.16090. Epub 2021 Jul 11. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34173336 Review.
Cited by
-
Cripto/GRP78 modulation of the TGF-β pathway in development and oncogenesis.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 4;586(14):1836-45. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.051. Epub 2012 Feb 1. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22306319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRIPTO/GRP78 signaling maintains fetal and adult mammary stem cells ex vivo.Stem Cell Reports. 2014 Apr 3;2(4):427-39. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.02.010. eCollection 2014 Apr 8. Stem Cell Reports. 2014. PMID: 24749068 Free PMC article.
-
ALK7 gene polymorphism is associated with metabolic syndrome risk and cardiovascular remodeling.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2013 Aug;101(2):134-40. doi: 10.5935/abc.20130148. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23765385 Free PMC article.
-
GDF3 Protects Mice against Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction and Mortality by Suppression of Macrophage Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype.Cells. 2020 Jan 3;9(1):120. doi: 10.3390/cells9010120. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31947892 Free PMC article.
-
Control of brown adipose tissue adaptation to nutrient stress by the activin receptor ALK7.Elife. 2020 May 5;9:e54721. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54721. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32366358 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

