Association of bone activity, calcium load, aortic stiffness, and calcifications in ESRD
- PMID: 18480316
- PMCID: PMC2518431
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007050622
Association of bone activity, calcium load, aortic stiffness, and calcifications in ESRD
Abstract
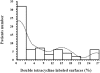
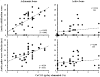
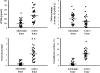
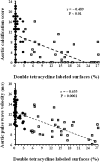
An inverse relationship between arterial calcifications and bone activity has been documented in patients with ESRD. Calcium overload is associated with arterial calcification, which is associated with arterial stiffening. Whether bone activity interacts with calcium load, aortic stiffness, or arterial calcification is unknown. This study assessed the impact of bone activity on the relationships between the dosage of calcium-containing phosphate binders and aortic stiffness (measured by pulse wave velocity) or abdominal aorta calcification score. Aortic stiffness and calcification were both positively associated with calcium load and negatively associated with bone activity. A significant interaction was found between dosage of calcium-containing phosphate binders and bone activity such that calcium load had a significantly greater influence on aortic calcifications and stiffening in the presence of adynamic bone disease. Independent of any other factor, including dosage of calcium-containing phosphate binders, adynamic bone was associated with greater aortic stiffening, suggesting cross-talk between the bone and arterial walls.
Figures
References
-
- Goodman WG, Goldin J, Kuizon BD, Yoon C, Gales B, Sider D, Wang Y, Chung J, Emerick A, Greaser L, Elashoff RB, Salusky I: Coronary artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med 342: 1478–1483, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Guérin AP, London GM, Marchais SJ, Métivier F: Arterial stiffening and vascular calcifications in end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15: 1014–1021, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Braun J, Oldendorf M, Moshage W, Heidler F, Zeitler E, Luft FC: Electron-beam computed tomography in the evaluation of cardiac calcifications in chronic dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 27: 394–401, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Block GA, Spiegal DM, Ehrlich J, Ravindra M, Lindbergh J, Dreisbach A, Raggi P: Effects of sevelamer and calcium on coronary artery calcification in patients new to hemodialysis. Kidney Int 68: 1815–1824, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, Kauppila LI, O'Donnell CJ, Kiel PD, Hannan M, Polak JM, Cupples A: Abdominal aortic calcific deposits are an important predictor of vascular morbidity and mortality. Circulation 103: 1529–1534, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

