Qualitative and quantitative characteristics of rotavirus-specific CD8 T cells vary depending on the route of infection
- PMID: 18480435
- PMCID: PMC2446946
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00450-08
Qualitative and quantitative characteristics of rotavirus-specific CD8 T cells vary depending on the route of infection
Abstract
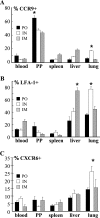
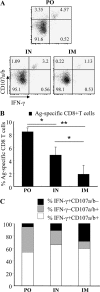
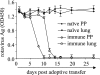
CD8 T-cell response provides an important defense against rotavirus, which infects a variety of systemic locations in addition to the gut. Here we investigated the distribution, phenotype, and function of rotavirus-specific CD8 T cells in multiple organs after rotavirus infection initiated via the intranasal, oral, or intramuscular route. The highest level of virus-specific CD8 T cells was observed in the Peyer's patches of orally infected mice and in the lungs of intranasally infected animals. Very low levels of virus-specific CD8 T cells were detected in peripheral blood or spleen irrespective of the route of infection. Rotavirus-specific CD8 T cells from Peyer's patches of orally infected mice expressed high levels of CCR9, while CXCR6 and LFA-1 expression was associated with virus-specific CD8 T cells in lungs of intranasally infected mice. Oral infection induced the highest proportion of gamma interferon(-) CD107a/b(+) CD8 T cells in Peyer's patches. When equal numbers of rotavirus-specific CD8 T cells were transferred into Rag-1 knockout mice chronically infected with rotavirus, the donor cells derived from Peyer's patches of orally infected mice were more efficient than those derived from lungs of intranasally infected animals in clearing intestinal infection. These results suggest that different routes of infection induce virus-specific CD8 T cells with distinct homing phenotypes and effector functions as well as variable abilities to clear infection.
Figures
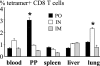
References
-
- Agnello, D., C. A. Herve, A. Lavaux, M. Darniot, P. Guillon, A. Charpilienne, and P. Pothier. 2006. Intrarectal immunization with rotavirus 2/6 virus-like particles induces an antirotavirus immune response localized in the intestinal mucosa and protects against rotavirus infection in mice. J. Virol. 803823-3832. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angel, J., M. A. Franco, and H. B. Greenberg. 2007. Rotavirus vaccines: recent developments and future considerations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5529-539. - PubMed
-
- Belyakov, I. M., M. A. Derby, J. D. Ahlers, B. L. Kelsall, P. Earl, B. Moss, W. Strober, and J. A. Berzofsky. 1998. Mucosal immunization with HIV-1 peptide vaccine induces mucosal and systemic cytotoxic T lymphocytes and protective immunity in mice against intrarectal recombinant HIV-vaccinia challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 951709-1714. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benson, J., C. Chougnet, M. Robert-Guroff, D. Montefiori, P. Markham, G. Shearer, R. C. Gallo, M. Cranage, E. Paoletti, K. Limbach, D. Venzon, J. Tartaglia, and G. Franchini. 1998. Recombinant vaccine-induced protection against the highly pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251: dependence on route of challenge exposure. J. Virol. 724170-4182. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Betts, M. R., J. M. Brenchley, D. A. Price, S. C. De Rosa, D. C. Douek, M. Roederer, and R. A. Koup. 2003. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 28165-78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

