Live-cell analysis of mitotic spindle formation in taxol-treated cells
- PMID: 18481305
- PMCID: PMC2753270
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20283
Live-cell analysis of mitotic spindle formation in taxol-treated cells
Abstract
Taxol functions to suppress the dynamic behavior of individual microtubules, and induces multipolar mitotic spindles. However, little is known about the mechanisms by which taxol disrupts normal bipolar spindle assembly in vivo. Using live imaging of GFP-alpha tubulin expressing cells, we examined spindle assembly after taxol treatment. We find that as taxol-treated cells enter mitosis, there is a dramatic re-distribution of the microtubule network from the centrosomes to the cell cortex. As they align there, the cortical microtubules recruit NuMA to their embedded ends, followed by the kinesin motor HSET. These cortical microtubules then bud off to form cytasters, which fuse into multipolar spindles. Cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin do not re-localize to cortical microtubules, and disruption of dynein/dynactin interactions by over-expression of p50 "dynamitin" does not prevent cytaster formation. Taxol added well before spindle poles begin to form induces multipolarity, but taxol added after nascent spindle poles are visible-but before NEB is complete-results in bipolar spindles. Our results suggest that taxol prevents rapid transport of key components, such as NuMA, to the nascent spindle poles. The net result is loss of mitotic spindle pole cohesion, microtubule re-distribution, and cytaster formation.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
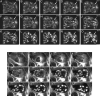
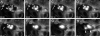
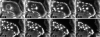

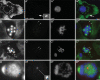

Similar articles
-
Formation of spindle poles by dynein/dynactin-dependent transport of NuMA.J Cell Biol. 2000 May 15;149(4):851-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.4.851. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10811826 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein-mediated assembly of pericentrin and gamma tubulin onto centrosomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Jun;11(6):2047-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.6.2047. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10848628 Free PMC article.
-
Dynein/dynactin regulate metaphase spindle length by targeting depolymerizing activities to spindle poles.J Cell Biol. 2004 Aug 16;166(4):465-71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200404015. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15314063 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NuMA in vertebrate cells: review of an intriguing multifunctional protein.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1137-46. doi: 10.2741/1868. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146802 Review.
-
[Dynein and dynactin as organizers of the system of cell microtubules].Ontogenez. 2006 Sep-Oct;37(5):323-39. Ontogenez. 2006. PMID: 17066975 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Dual role of deubiquitinating enzyme USP19 regulates mitotic progression and tumorigenesis by stabilizing survivin.Mol Ther. 2022 Nov 2;30(11):3414-3429. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.07.019. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35918893 Free PMC article.
-
The taccalonolides and paclitaxel cause distinct effects on microtubule dynamics and aster formation.Mol Cancer. 2014 Feb 28;13:41. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-41. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24576146 Free PMC article.
-
Cells satisfy the mitotic checkpoint in Taxol, and do so faster in concentrations that stabilize syntelic attachments.J Cell Biol. 2009 Sep 7;186(5):675-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200906150. Epub 2009 Aug 31. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19720871 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and anticancer activity of all known (-)-agelastatin alkaloids.J Org Chem. 2013 Dec 6;78(23):11970-84. doi: 10.1021/jo4020112. Epub 2013 Nov 21. J Org Chem. 2013. PMID: 24152243 Free PMC article.
-
How Taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Sep 15;25(18):2677-81. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0916. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 25213191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin-Hanjani S, Wadsworth P. Inhibition of spindle elongation by taxol. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;20:136–144. - PubMed
-
- Compton DA. Focusing on spindle poles. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:1477–1481. - PubMed
-
- Compton DA, Cleveland DW. NuMA, a nuclear protein involved in mitosis and nuclear reformation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:343–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

