Protective effects of cilostazol against transient focal cerebral ischemia and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion injury
- PMID: 18482026
- PMCID: PMC6494013
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2008.00042.x
Protective effects of cilostazol against transient focal cerebral ischemia and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion injury
Abstract
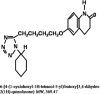
Cilostazol increases intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) levels by inhibiting type III phosphodiesterase. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of intermittent claudication. Its principal actions include inhibition of platelet aggregation, antithrombotic action in cerebral ischemia, and vasodilation, mediated by increased cyclic AMP levels. In a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, cilostazol has been shown to protect patients from recurrent cerebral infarction. It has been recently suggested that cilastozol could be useful in the treatment of transient focal cerebral ischemic injury. Beneficial effects of cilostazol in cerebral ischemic infarction and edema formation has been confirmed in rats by the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The preventive effect was ascribed to cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)-coupled maxi-K channel activation with additional antioxidant and poly(adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerase inhibitory actions. Most recently, cilostazol has been shown to prevent vacuolation and rarefaction in the white matter of the rats subjected to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in association with suppression of astrocyte and microglial activation. Taken together, recent experimental studies with cilostazol showed promising results in cerebral ischemia and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aizawa T, Wei H, Miano JM, Abe J, Berk BC, Yan C (2003) Role of phosphodiesterase 3 in NO/cGMP‐mediated antiinflammatory effects in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 93: 406–413. - PubMed
-
- Akiguchi I, Tomimoto H, Suenaga T, Wakita H, Budka H (1997) Alterations in glia and axons in the brains of Binswanger's disease patients. Stroke 28: 1423–1429. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Kudo S, Shimizu T (1985) The absorption, distribution and excretion of a new antithrombotic and vasodilating agent, cilostazol, in rat, rabbit, dog and man. Arzneimittelforschung 35: 1124–1132. - PubMed
-
- Bednar MM (2000) Stroke: Antithrombin versus anti‐platelet therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9: 355–369. - PubMed
-
- Betz AL (1996) Alterations in cerebral endothelial cell function in ischemia. Adv Neurol 71: 301–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

