Chemopreventive efficacy of inositol hexaphosphate against prostate tumor growth and progression in TRAMP mice
- PMID: 18483386
- PMCID: PMC3049549
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5275
Chemopreventive efficacy of inositol hexaphosphate against prostate tumor growth and progression in TRAMP mice
Abstract
Purpose: Herein, for the first time, we evaluated the in vivo chemopreventive efficacy of inositol hexaphosphate (IP6), a major constituent of high-fiber diets, against prostate tumor growth and progression in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model.
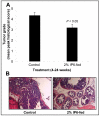
Experimental design: Beginning at 4 weeks of age, male TRAMP mice were fed 2% (w/v) IP6 in drinking water or only drinking water till 24 weeks of age, and then sacrificed. Prostate tissue was subjected to histopathologic analysis and to immunohistochemical analyses for proliferation and apoptosis.
Results: IP6 feeding did not show any adverse effect on fluid and diet consumption and body weight. There was a significant reduction (40%; P < 0.01) in lower urogenital tract weight in IP6-fed mice. IP6 inhibited prostate cancer progression at prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia stage and strongly reduced the incidence of adenocarcinoma (prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia/adenocarcinoma, 75:25% in the IP6 group versus 39:61% in the control group; P < 0.05). The incidences of well-differentiated and poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas in the IP6-fed group were reduced by 44% and 62%, respectively. Immunohistochemical analysis of prostate tissue showed a 26% decrease (P < 0.05) in proliferation cell nuclear antigen-positive cells and a 3.5-fold increase in apoptotic cells with no effect on Tag expression by IP6.
Conclusions: These findings are both novel and highly significant in establishing for the first time that oral IP6, without any toxicity, suppresses prostate tumor growth and progression at the neoplastic stage, thereby reducing the incidence of adenocarcinoma through its antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects, and thus indicating that IP6 could have potential chemopreventive effects against human prostate cancer.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Inositol hexaphosphate inhibits tumor growth, vascularity, and metabolism in TRAMP mice: a multiparametric magnetic resonance study.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 Jan;6(1):40-50. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0387. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23213071 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo suppression of hormone-refractory prostate cancer growth by inositol hexaphosphate: induction of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jan 1;10(1 Pt 1):244-50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-1080-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 14734476
-
Growth inhibitory and apoptotic effects of inositol hexaphosphate in transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate (TRAMP-C1) cells.Int J Oncol. 2003 Nov;23(5):1413-8. Int J Oncol. 2003. PMID: 14532984
-
Prostate cancer and inositol hexaphosphate: efficacy and mechanisms.Anticancer Res. 2005 Jul-Aug;25(4):2891-903. Anticancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16080543 Review.
-
Inositol Hexaphosphate (IP6) and Colon Cancer: From Concepts and First Experiments to Clinical Application.Molecules. 2020 Dec 15;25(24):5931. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245931. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33333775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of inositol hexaphosphate on the development of UVB-induced skin tumors in SKH1 hairless mice.Comp Med. 2009 Apr;59(2):147-52. Comp Med. 2009. PMID: 19389306 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid metabolism and ALDH1A2 (RALDH2) expression are altered in the transgenic adenocarcinoma mouse prostate model.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Nov 1;78(9):1127-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.022. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19549509 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of inositol hexaphosphate on the expression of selected metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in IL-1β-stimulated colon cancer cells.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012 Nov;27(11):1419-28. doi: 10.1007/s00384-012-1445-3. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012. PMID: 22415590 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in cellular levels of inositol polyphosphates during apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Dec;345(1-2):61-8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0560-0. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20725767
-
Stage-Specific Effect of Inositol Hexaphosphate on Cancer Stem Cell Pool during Growth and Progression of Prostate Tumorigenesis in TRAMP Model.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;14(17):4204. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174204. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shamsuddin AM, Vucenik I, Cole KE. IP6: a novel anti-cancer agent. Life Sci. 1997;61:343–54. - PubMed
-
- Vucenik I, Shamsuddin AM. Cancer inhibition by inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) and inositol: from laboratory to clinic. J Nutr. 2003;133:3778S–84S. - PubMed
-
- Singh RP, Agarwal R. Prostate cancer and inositol hexaphosphate: efficacy and mechanisms. Anticancer Res. 2005;25:2891–903. - PubMed
-
- Graf E, Eaton JW. Antioxidant functions of phytic acid. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;8:61–9. - PubMed
-
- Jariwalla RJ. Rice-bran products: phytonutrients with potential applications in preventive and clinical medicine. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 2001;27:17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

