Conditional deletion of Krüppel-like factor 4 delays downregulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation markers but accelerates neointimal formation following vascular injury
- PMID: 18483411
- PMCID: PMC2633447
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.176974
Conditional deletion of Krüppel-like factor 4 delays downregulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation markers but accelerates neointimal formation following vascular injury
Abstract
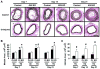
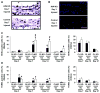
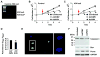
Phenotypic switching of smooth muscle cells (SMCs) plays a key role in vascular proliferative diseases. We previously showed that Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) suppressed SMC differentiation markers in cultured SMCs. Here, we derive mice deficient for Klf4 by conditional gene ablation and analyze their vascular phenotype following carotid injury. Klf4 expression was rapidly induced in SMCs of control mice after vascular injury but not in Klf4-deficient mice. Injury-induced repression of SMC differentiation markers was transiently delayed in Klf4-deficient mice. Klf4 mutant mice exhibited enhanced neointimal formation in response to vascular injury caused by increased cellular proliferation in the media but not an altered apoptotic rate. Consistent with these findings, cultured SMCs overexpressing Klf4 showed reduced cellular proliferation, in part, through the induction of the cell cycle inhibitor, p21(WAF1/Cip1) via increased binding of Klf4 and p53 to the p21(WAF1/Cip1) promoter/enhancer. In vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation assays also showed increased Klf4 binding to the promoter/enhancer regions of the p21(WAF1/Cip1) gene and SMC differentiation marker genes following vascular injury. Taken together, we have demonstrated that Klf4 plays a critical role in regulating expression of SMC differentiation markers and proliferation of SMCs in vivo in response to vascular injury.
Figures


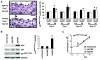

Comment in
-
Kruppel-like factor 4: transcriptional regulator of proliferation, or inflammation, or differentiation, or all three?Circ Res. 2008 Jun 20;102(12):1455-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.178954. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18566311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Kruppel-like factor 4: transcriptional regulator of proliferation, or inflammation, or differentiation, or all three?Circ Res. 2008 Jun 20;102(12):1455-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.178954. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18566311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Deletion of Krüppel-like factor 4 in endothelial and hematopoietic cells enhances neointimal formation following vascular injury.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Jan 27;3(1):e000622. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000622. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24470523 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative binding of KLF4, pELK-1, and HDAC2 to a G/C repressor element in the SM22α promoter mediates transcriptional silencing during SMC phenotypic switching in vivo.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 31;111(6):685-96. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.269811. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22811558 Free PMC article.
-
Role of specific microRNAs in regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and the response to injury.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010 Jun;3(3):246-50. doi: 10.1007/s12265-010-9163-0. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20543900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin and differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells.J Physiol. 2015 Jul 15;593(14):3013-30. doi: 10.1113/JP270033. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25952975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Smooth and cardiac muscle-selective knock-out of Kruppel-like factor 4 causes postnatal death and growth retardation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 2;285(27):21175-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.112482. Epub 2010 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20439457 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-derived miR-223 promotes a phenotypic switch in arterial injury repair.J Clin Invest. 2019 Mar 1;129(3):1372-1386. doi: 10.1172/JCI124508. Epub 2019 Feb 18. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30645204 Free PMC article.
-
Klf4, Klf2, and Zfp148 activate autophagy-related genes in smooth muscle cells during aortic aneurysm formation.Physiol Rep. 2019 Apr;7(8):e14058. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14058. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31025534 Free PMC article.
-
Klf4 has an unexpected protective role in perivascular cells within the microvasculature.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Aug 1;315(2):H402-H414. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00084.2018. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29631369 Free PMC article.
-
Anemoside B4 attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm by limiting smooth muscle cell transdifferentiation and its mediated inflammation.Front Immunol. 2024 May 31;15:1412022. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1412022. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38881898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Adam PJ, Regan CP, Hautmann MB, Owens GK. Positive- and negative-acting Krüppel-like transcription factors bind a transforming growth factor β control element required for expression of the smooth muscle cell differentiation marker SM22α in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:37798–37806. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Sinha S, Owens G. A transforming growth factor-β control element required for SM α-actin expression in vivo also partially mediates GKLF-dependent transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:48004–48011. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Sinha S, McDonald OG, Shang Y, Hoofnagle MH, Owens GK. Kruppel-like factor 4 abrogates myocardin-induced activation of smooth muscle gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:9719–9727. - PubMed
-
- Pidkovka NA, Cherepanova OA, Yoshida T, Alexander MR, Deaton RA, Thomas JA, Leitinger N, Owens GK. Oxidized phospholipids induce phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. Circ Res. 2007;101:792–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

