The uptake of apoptotic cells drives Coxiella burnetii replication and macrophage polarization: a model for Q fever endocarditis
- PMID: 18483547
- PMCID: PMC2361190
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000066
The uptake of apoptotic cells drives Coxiella burnetii replication and macrophage polarization: a model for Q fever endocarditis
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: The Uptake of Apoptotic Cells Drives Coxiella burnetii Replication and Macrophage Polarization: A Model for Q Fever Endocarditis.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Dec 13;18(12):e1011029. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011029. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36512518 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
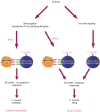
Patients with valvulopathy have the highest risk to develop infective endocarditis (IE), although the relationship between valvulopathy and IE is not clearly understood. Q fever endocarditis, an IE due to Coxiella burnetii, is accompanied by immune impairment. Patients with valvulopathy exhibited increased levels of circulating apoptotic leukocytes, as determined by the measurement of active caspases and nucleosome determination. The binding of apoptotic cells to monocytes and macrophages, the hosts of C. burnetii, may be responsible for the immune impairment observed in Q fever endocarditis. Apoptotic lymphocytes (AL) increased C. burnetii replication in monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages in a cell-contact dependent manner, as determined by quantitative PCR and immunofluorescence. AL binding induced a M2 program in monocytes and macrophages stimulated with C. burnetii as determined by a cDNA chip containing 440 arrayed sequences and functional tests, but this program was in part different in monocytes and macrophages. While monocytes that had bound AL released high levels of IL-10 and IL-6, low levels of TNF and increased CD14 expression, macrophages that had bound AL released high levels of TGF-beta1 and expressed mannose receptor. The neutralization of IL-10 and TGF-beta1 prevented the replication of C. burnetii due to the binding of AL, suggesting that they were critically involved in bacterial replication. In contrast, the binding of necrotic cells to monocytes and macrophages led to C. burnetii killing and typical M1 polarization. Finally, interferon-gamma corrected the immune deactivation induced by apoptotic cells: it prevented the replication of C. burnetii and re-directed monocytes and macrophages toward a M1 program, which was deleterious for C. burnetii. We suggest that leukocyte apoptosis associated with valvulopathy may be critical for the pathogenesis of Q fever endocarditis by deactivating immune cells and creating a favorable environment for bacterial persistence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
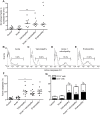
References
-
- Durack DT. Prevention of infective endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Wilson W, Taubert KA, Gewitz M, Lockhart PB, Baddour LM, et al. Prevention of infective endocarditis: guidelines from the American Heart Association: a guideline from the American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. J Am Dent Assoc. 2007;138:747–760. - PubMed
-
- Hamill RJ. Role of fibronectin in infective endocarditis. Rev Infect Dis. 1987;9(Suppl 4):S360–371. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

