A genome-wide association study identifies novel alleles associated with hair color and skin pigmentation
- PMID: 18483556
- PMCID: PMC2367449
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000074
A genome-wide association study identifies novel alleles associated with hair color and skin pigmentation
Abstract
We conducted a multi-stage genome-wide association study of natural hair color in more than 10,000 men and women of European ancestry from the United States and Australia. An initial analysis of 528,173 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) genotyped on 2,287 women identified IRF4 and SLC24A4 as loci highly associated with hair color, along with three other regions encompassing known pigmentation genes. We confirmed these associations in 7,028 individuals from three additional studies. Across these four studies, SLC24A4 rs12896399 and IRF4 rs12203592 showed strong associations with hair color, with p = 6.0x10(-62) and p = 7.46x10(-127), respectively. The IRF4 SNP was also associated with skin color (p = 6.2x10(-14)), eye color (p = 6.1x10(-13)), and skin tanning response to sunlight (p = 3.9x10(-89)). A multivariable analysis pooling data from the initial GWAS and an additional 1,440 individuals suggested that the association between rs12203592 and hair color was independent of rs1540771, a SNP between the IRF4 and EXOC2 genes previously found to be associated with hair color. After adjustment for rs12203592, the association between rs1540771 and hair color was not significant (p = 0.52). One variant in the MATP gene was associated with hair color. A variant in the HERC2 gene upstream of the OCA2 gene showed the strongest and independent association with hair color compared with other SNPs in this region, including three previously reported SNPs. The signals detected in a region around the MC1R gene were explained by MC1R red hair color alleles. Our results suggest that the IRF4 and SLC24A4 loci are associated with human hair color and skin pigmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
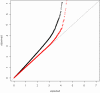
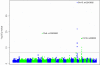
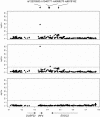
References
-
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of human skin coloration. J Hum Evol. 2000;39:57–106. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ. Risk factors for skin cancers: a nested case-control study within the Nurses' Health Study. Int J Epidemiol. 2006;35:1514–1521. - PubMed
-
- Clark P, Stark AE, Walsh RJ, Jardine R, Martin NG. A twin study of skin reflectance. Ann Hum Biol. 1981;8:529–541. - PubMed
-
- Frisancho AR, Wainwright R, Way A. Heritability and components of phenotypic expression in skin reflectance of Mestizos from the Peruvian lowlands. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1981;55:203–208. - PubMed
-
- Harrison GA, Owen JJ. Studies on the inheritance of human skin colour. Ann Hum Genet. 1964;28:27–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA88363/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA132175/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128080/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA088363/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA128080/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA132175/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

