Injection of CART (cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript) peptide into the nucleus accumbens reduces cocaine self-administration in rats
- PMID: 18485497
- PMCID: PMC2497435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.03.039
Injection of CART (cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript) peptide into the nucleus accumbens reduces cocaine self-administration in rats
Abstract
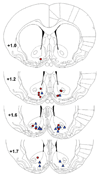
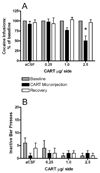
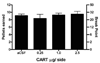
Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptides appear to modulate various effects of psychostimulant drugs. Injections of CART peptide into the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) inhibit locomotion produced by systemic injections of the psychostimulants cocaine and amphetamine. Intra-NAcc injections of CART peptide also inhibit locomotion produced by microinfusions of dopamine into the NAcc, suggesting that the effects of CART peptides may be due to an interaction with the dopaminergic system in the NAcc. We sought to determine if this inhibitory effect of CART peptide generalizes to other measures of dopaminergic function such as reward/reinforcement by testing the effect of bilateral intra-NAcc CART infusions (0, 0.25, 1.0 and 2.5 microg per side) on cocaine and food self-administration. One group of rats self-administered cocaine (0.75 mg/kg per 140 microl IV infusion) on a progressive ratio schedule. A separate group received 45 mg food pellets on the same progressive ratio schedule. Bilateral intra-NAcc injections of CART peptide dose-dependently decreased the number of cocaine infusions, the breakpoint of cocaine self-administration, and the total number of bar presses on the cocaine-associated lever. There were no effects of CART injections on the breakpoint for food reward. Thus, we conclude that injections of CART into the NAcc appear to functionally antagonize a major site of action for cocaine self-administration in rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microinjection of CART peptide 55-102 into the nucleus accumbens blocks both the expression of behavioral sensitization and ERK phosphorylation by cocaine.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Aug;53(2):344-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.05.014. Epub 2007 May 29. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17610912
-
Microinjection of CART (cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript) peptide into the nucleus accumbens inhibits the cocaine-induced upregulation of dopamine receptors and locomotor sensitization.Neurochem Int. 2014 Sep;75:105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24953280
-
CART peptide 55-102 microinjected into the nucleus accumbens inhibits the expression of behavioral sensitization by amphetamine.Regul Pept. 2007 Dec 4;144(1-3):6-9. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.07.003. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Regul Pept. 2007. PMID: 17706801
-
CART peptides as modulators of dopamine and psychostimulants and interactions with the mesolimbic dopaminergic system.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Jan 1;75(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.028. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17854774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of CART in the reward/reinforcing properties of psychostimulants.Peptides. 2006 Aug;27(8):1993-2004. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.03.034. Peptides. 2006. PMID: 16766084 Review.
Cited by
-
CART Peptides and Drugs of Abuse: A Review of Recent Progress.J Drug Alcohol Res. 2016;5:235984. doi: 10.4303/jdar/235984. Epub 2016 Jun 28. J Drug Alcohol Res. 2016. PMID: 29238623 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine Induces TET1- and TET3-Dependent DNA Hydroxymethylation of Crh and Avp Genes in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;55(6):5154-5166. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0750-9. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28842817 Free PMC article.
-
CART peptides: regulators of body weight, reward and other functions.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008 Oct;9(10):747-58. doi: 10.1038/nrn2493. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18802445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inhibition of cocaine-induced locomotor activity by CART 55-102 is lost after repeated cocaine administration.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Aug 29;550:179-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.039. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23819981 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hypocretin in driving arousal and goal-oriented behaviors.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:103-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.11.054. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19948148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- National Research Council of the National Academies. Guidelines for the Care and Use of Mammals in Neuroscience and Behavioral Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2003. - PubMed
-
- Aja S, Sahandy S, Ladenheim EE, Schwartz GJ, Moran TH. Intracerebroventricular CART peptide reduces food intake and alters motor behavior at a hindbrain site. Am J Physiol Regulat Integrat Comp Physiol. 2001;281:R1862–R1867. - PubMed
-
- Bannon AW, Seda J, Carmouche M, Francis JM, Jarosinski MA, Douglass J. Multiple behavioral effects of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptides in mice: CART 42–89 and CART 49–89 differ in potency and activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;299:1021–1026. - PubMed
-
- Beaudry G, Zekki H, Rouillard C, Levesque D. Clozapine and dopamine D3 receptor antisense reduce cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript expression in the rat nucleus accumbens shell. Synapse. 2004;51:233–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

