Acetylation is indispensable for p53 activation
- PMID: 18485870
- PMCID: PMC2914560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.025
Acetylation is indispensable for p53 activation
Erratum in
- Cell. 2008 Jun 27;133(7):1290
Abstract
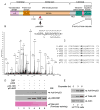
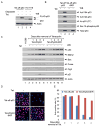
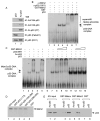
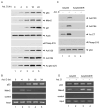
The activation of the tumor suppressor p53 facilitates the cellular response to genotoxic stress; however, the p53 response can only be executed if its interaction with its inhibitor Mdm2 is abolished. There have been conflicting reports on the question of whether p53 posttranslational modifications, such as phosphorylation or acetylation, are essential or only play a subtle, fine-tuning role in the p53 response. Thus, it remains unclear whether p53 modification is absolutely required for its activation. We have now identified all major acetylation sites of p53. Although unacetylated p53 retains its ability to induce the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop, loss of acetylation completely abolishes p53-dependent growth arrest and apoptosis. Notably, acetylation of p53 abrogates Mdm2-mediated repression by blocking the recruitment of Mdm2 to p53-responsive promoters, which leads to p53 activation independent of its phosphorylation status. Our study identifies p53 acetylation as an indispensable event that destabilizes the p53-Mdm2 interaction and enables the p53-mediated stress response.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tip60-dependent acetylation of p53 modulates the decision between cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis.Mol Cell. 2006 Dec 28;24(6):827-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.11.021. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 17189186
-
Mdm2 is required for inhibition of Cdk2 activity by p21, thereby contributing to p53-dependent cell cycle arrest.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;27(11):4166-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01967-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17371838 Free PMC article.
-
SMAR1 forms a ternary complex with p53-MDM2 and negatively regulates p53-mediated transcription.J Mol Biol. 2009 May 15;388(4):691-702. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.033. Epub 2009 Mar 19. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19303885
-
The p53 orchestra: Mdm2 and Mdmx set the tone.Trends Cell Biol. 2010 May;20(5):299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Trends Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20172729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of p53: a collaboration between Mdm2 and Mdmx.Oncotarget. 2012 Mar;3(3):228-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.443. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22410433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A human tRNA synthetase is a potent PARP1-activating effector target for resveratrol.Nature. 2015 Mar 19;519(7543):370-3. doi: 10.1038/nature14028. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25533949 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) in hepatocellular carcinoma: a potential therapeutic target.Tumour Biol. 2015 Jun;36(6):4063-74. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3488-x. Epub 2015 May 1. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25926383 Review.
-
Negative regulation of the p300-p53 interplay by DDX24.Oncogene. 2016 Jan 28;35(4):528-36. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.77. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25867071 Free PMC article.
-
ING Proteins: Tumour Suppressors or Oncoproteins.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 27;13(9):2110. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092110. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Janus Face of p53-Targeting Ubiquitin Ligases.Cells. 2020 Jul 9;9(7):1656. doi: 10.3390/cells9071656. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32660118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An W, Kim J, Roeder RG. Ordered cooperative functions of PRMT1, p300, and CARM1 in transcriptional activation by p53. Cell. 2004;117:735–748. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio O, Geisberg JV, Struhl K. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation for determining the association of proteins with specific genomic sequences in vivo. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2004;17:7.1–7.23. - PubMed
-
- Arva NC, Gopen TR, Talbott KE, Campbell LE, Chicas A, White DE, Bond GL, Levine AJ, Bargonetti J. A chromatin-associated and transcriptionally inactive p53-Mdm2 complex occurs in Mdm2 SNP309 homozygous cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26776–26787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

