Helium-3 diffusion MR imaging of the human lung over multiple time scales
- PMID: 18486006
- PMCID: PMC2494939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2007.10.009
Helium-3 diffusion MR imaging of the human lung over multiple time scales
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with hyperpolarized (3)He gas is a powerful technique for probing the characteristics of the lung microstructure. A key parameter for this technique is the diffusion time, which is the period during which the atoms are allowed to diffuse within the lung for measurement of the signal attenuation. The relationship between diffusion time and the length scales that can be explored is discussed, and representative, preliminary results are presented from ongoing studies of the human lung for diffusion times ranging from milliseconds to several seconds.
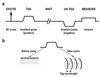
Materials and methods: (3)He diffusion MRI of the human lung was performed on a 1.5T Siemens Sonata scanner. Using gradient echo-based and stimulated echo-based techniques for short and medium-to-long diffusion times, respectively, measurements were performed for times ranging from 2 milliseconds to 6.5 seconds in two healthy subjects, a subject with subclinical chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and a subject with bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
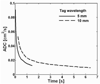
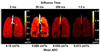
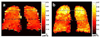
Results: In healthy subjects, the apparent diffusion coefficient decreased by about 10-fold, from approximately 0.2 to 0.02 cm(2)/second, as the diffusion time increased from approximately 1 millisecond to 1 second. Results in subjects with disease suggest that measurements made at diffusion times substantially longer than 1 millisecond may provide improved sensitivity for detecting certain pathologic changes in the lung microstructure.
Conclusions: With appropriately designed pulse sequences it is possible to explore the diffusion of hyperpolarized (3)He in the human lung over more than a 1,000-fold variation of the diffusion time. Such measurements provide a new opportunity for exploring and characterizing the microstructure of the healthy and diseased lung.
Figures
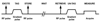

References
-
- Moller HE, Chen XJ, Saam B, et al. MRI of the lungs using hyperpolarized noble gases. Magn Reson Med. 2002;47(6):1029–1051. - PubMed
-
- van Beek EJ, Wild JM, Kauczor HU, et al. Functional MRI of the lung using hyperpolarized 3-helium gas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;20(4):540–554. - PubMed
-
- Altes TA, Powers PL, Knight-Scott J, et al. Hyperpolarized 3He MR lung ventilation imaging in asthmatics: preliminary findings. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13(3):378–384. - PubMed
-
- de Lange EE, Altes TA, Patrie JT, et al. Evaluation of asthma with hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI: correlation with clinical severity and spirometry. Chest. 2006;130(4):1055–1062. - PubMed
-
- Saam BT, Yablonskiy DA, Kodibagkar VD, et al. MR imaging of diffusion of 3He gas in healthy and diseased lungs. Magn Reson Med. 2000;44(2):174–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

