The blood-brain barrier: connecting the gut and the brain
- PMID: 18486244
- PMCID: PMC2553040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.08.027
The blood-brain barrier: connecting the gut and the brain
Abstract
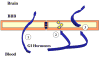
The BBB prevents the unrestricted exchange of substances between the central nervous system (CNS) and the blood. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) also conveys information between the CNS and the gastrointestinal (GI) tract through several mechanisms. Here, we review three of those mechanisms. First, the BBB selectively transports some peptides and regulatory proteins in the blood-to-brain or the brain-to-blood direction. The ability of GI hormones to affect functions of the BBB, as illustrated by the ability of insulin to alter the BBB transport of amino acids and drugs, represents a second mechanism. A third mechanism is the ability of GI hormones to affect the secretion by the BBB of substances that themselves affect feeding and appetite, such as nitric oxide and cytokines. By these and other mechanisms, the BBB regulates communications between the CNS and GI tract.
Figures

References
-
- Smith GP, Gibbs J, Jerome C, Pi-Sunyer FX, Kissileff HR, Thornton J. The satiety effect of cholecystokinin: a progress report. Peptides. 1981;2 2:57–59. - PubMed
-
- Kelley KW, Bluthe RM, Dantzer R, Zhou JH, Shen WH, Johnson RW, Broussard SR. Cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2003;17:S112–S118. - PubMed
-
- Romeo HE, Tio DL, Rahman SU, Chiappelli F, Taylor AN. The glossopharyngeal nerve as a novel pathway in immune-to-brain communication: relevance to neuroimmune surveillance of the oral cavity. J Neuroimmunol. 2001;115:91–100. - PubMed
-
- Watkins LR, Maier SF, Goehler LE. Cytokine-to-brain communication: a review & analysis of alternative mechanisms. Life Sci. 1995;57:1011–1026. - PubMed
-
- Davson H, Segal MB. Physiology of the CSF and Blood-Brain Barriers. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

