Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery
- PMID: 18486268
- PMCID: PMC2720159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.03.005
Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery
Abstract
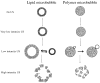
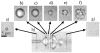
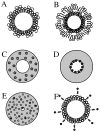
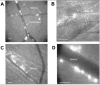
Ultrasound contrast agents, in the form of gas-filled microbubbles, are becoming popular in perfusion monitoring; they are employed as molecular imaging agents. Microbubbles are manufactured from biocompatible materials, they can be injected intravenously, and some are approved for clinical use. Microbubbles can be destroyed by ultrasound irradiation. This destruction phenomenon can be applied to targeted drug delivery and enhancement of drug action. The ultrasonic field can be focused at the target tissues and organs; thus, selectivity of the treatment can be improved, reducing undesirable side effects. Microbubbles enhance ultrasound energy deposition in the tissues and serve as cavitation nuclei, increasing intracellular drug delivery. DNA delivery and successful tissue transfection are observed in the areas of the body where ultrasound is applied after intravascular administration of microbubbles and plasmid DNA. Accelerated blood clot dissolution in the areas of insonation by cooperative action of thrombolytic agents and microbubbles is demonstrated in several clinical trials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrasonic drug delivery--a general review.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2004 Nov;1(1):37-56. doi: 10.1517/17425247.1.1.37. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2004. PMID: 16296719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on cavitation enhanced endothelial layer permeability.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 Aug 1;168:83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.02.027. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 29486912 Review.
-
Nucleic acid delivery with microbubbles and ultrasound.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014 Jun;72:82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014. PMID: 24486388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbubbles as ultrasound triggered drug carriers.J Pharm Sci. 2009 Jun;98(6):1935-61. doi: 10.1002/jps.21571. J Pharm Sci. 2009. PMID: 18979536 Review.
-
[Recent advances in the applications of ultrasonic microbubbles as gene delivery systems].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Feb;42(2):127-31. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17518038 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Control of CD8 T-Cell Infiltration into Tumors by Vasculature and Microenvironment.Adv Cancer Res. 2015;128:263-307. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Adv Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26216636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Augmentation of transgenic expression by ultrasound‑mediated liposome microbubble destruction.Mol Med Rep. 2012 Apr;5(4):964-70. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.766. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22294278 Free PMC article.
-
Microbubbles used for contrast enhanced ultrasound and theragnosis: a review of principles to applications.Biomed Eng Lett. 2017 Feb 14;7(2):59-69. doi: 10.1007/s13534-017-0016-5. eCollection 2017 May. Biomed Eng Lett. 2017. PMID: 30603152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cancers Using Chlorotoxin Nanoparticles.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;15(13):3388. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133388. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography: Review and Applications.Cureus. 2021 Sep 24;13(9):e18243. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18243. eCollection 2021 Sep. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34712527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kassan DG, Lynch AM, Stiller MJ. Physical enhancement of dermatologic drug delivery: Iontophoresis and phonophoresis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:657–66. - PubMed
-
- Gramiak R, Shah PM. Echocardiography of the aortic root. Invest Radiol. 1968;3:356–66. - PubMed
-
- Feinstein SB, Ten Cate FJ, Zwehl W, Ong K, Maurer G, Tei C, Shah PM, Meerbaum S, Corday E. Two-dimensional contrast echocardiography. I. In vitro development and quantitative analysis of echo contrast agents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984;3:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Ten Cate FJ, Feinstein S, Zwehl W, Meerbaum S, Fishbein M, Shah PM, Corday E. Two-dimensional contrast echocardiography. Ii. Transpulmonary studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984;3:21–7. - PubMed
-
- Kabalnov A, Klein D, Pelura T, Schutt E, Weers J. Dissolution of multicomponent microbubbles in the bloodstream: 1. Theory. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1998;24:739–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

