Snapshot gradient-recalled echo-planar images of rat brains at long echo time at 9.4 T
- PMID: 18486393
- PMCID: PMC2646166
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2008.01.009
Snapshot gradient-recalled echo-planar images of rat brains at long echo time at 9.4 T
Abstract
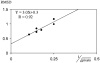
With improved B 0 homogeneity along with satisfactory gradient performance at high magnetic fields, snapshot gradient-recalled echo-planar imaging (GRE-EPI) would perform at long echo times (TEs) on the order of T2*, which intrinsically allows obtaining strongly T2*-weighted images with embedded substantial anatomical details in ultrashort time. The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility and quality of long TE snapshot GRE-EPI images of rat brain at 9.4 T. When compensating for B 0 inhomogeneities, especially second-order shim terms, a 200 x 200 microm2 in-plane resolution image was reproducibly obtained at long TE (>25 ms). The resulting coronal images at 30 ms had diminished geometric distortions and, thus, embedded substantial anatomical details. Concurrently with the very consistent stability, such GRE-EPI images should permit to resolve functional data not only with high specificity but also with substantial anatomical details, therefore allowing coregistration of the acquired functional data on the same image data set.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Compressed sensing fMRI using gradient-recalled echo and EPI sequences.Neuroimage. 2014 May 15;92:312-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.045. Epub 2014 Feb 2. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24495813 Free PMC article.
-
Functional MRI in human subjects with gradient-echo and spin-echo EPI at 9.4 T.Magn Reson Med. 2014 Jan;71(1):209-18. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24656. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Magn Reson Med. 2014. PMID: 23447097
-
Fast susceptibility-weighted imaging with three-dimensional short-axis propeller (SAP)-echo-planar imaging.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 May;41(5):1447-53. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24675. Epub 2014 Jun 23. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 24956237 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ferucarbotran-enhanced fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery echo-planar, T2-weighted turbo spin-echo, T2*-weighted gradient-echo, and diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging for detection of malignant liver lesions.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 Mar;31(3):607-16. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22098. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20187203
-
Comparison of gradient-recalled echo and spin-echo echo-planar imaging MR elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2018 Apr;28(4):1709-1718. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5149-5. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29164384 Review.
References
-
- Tkac I, Henry PG, Andersen P, Keene CD, Low WC, Gruetter R. Highly resolved in vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy of the mouse brain at 9.4 T. Magn Reson Med. 2004;52(3):478–84. - PubMed
-
- Tkac I, Starcuk Z, Choi IY, Gruetter R. In vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy of rat brain at 1 ms echo time. Magn Reson Med. 1999;41(4):649–56. - PubMed
-
- Silva AC, Kim SG, Garwood M. Imaging blood flow in brain tumors using arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med. 2000;44(2):169–73. - PubMed
-
- Silva AC, Zhang W, Williams DS, Koretsky AP. Multi-slice MRI of rat brain perfusion during amphetamine stimulation using arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med. 1995;33(2):209–14. - PubMed
-
- Zhu XH, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Ugurbil K, Chen W. In vivo 17O NMR approaches for brain study at high field. NMR Biomed. 2005;18(2):83–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

