Peptide YY (PYY) levels and bone mineral density (BMD) in women with anorexia nervosa
- PMID: 18486583
- PMCID: PMC2493518
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.03.007
Peptide YY (PYY) levels and bone mineral density (BMD) in women with anorexia nervosa
Abstract
Introduction: Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a psychiatric illness that results in significant bone loss. Studies examining the neuroendocrine dysregulation that occurs in AN may increase understanding of endocrine systems that regulate bone mass. Peptide YY (PYY) is an anorexigenic peptide derived primarily from the intestine, with actions mediated via activation of Y receptors. We have previously shown that PYY levels are elevated in adolescents with AN. Y2 receptor knockout mice have increased bone mineral density (BMD) and thus PYY may play a role in regulating bone mass. We hypothesized that PYY levels would be inversely associated with BMD in women with AN.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study performed in a General Clinical Research Center of 12 adult women with AN, (mean+/-SEM) mean age 30.9+/-1.8 years, BMI 17.1+/-0.4 kg/m2, and % ideal body weight 77.5+/-1.7%. PYY concentrations were measured hourly from 20:00 h to 08:00 h. BMD was measured using dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
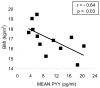
Results: In women with AN, mean overnight PYY levels strongly inversely correlated with BMD at the PA spine (r=-0.77, p=0.003), lateral spine (r=-0.82, p=0.002), total hip (r=-0.75, p=0.005), femoral neck (r=-0.72, p=0.009), total radius (r=-0.72, p=0.009) and 1/3 distal radius (r=-0.81, p=0.002). Body mass index was inversely correlated with PYY level (r=-0.64, p=0.03). Multivariate stepwise regression analysis was performed to determine the contribution of age, duration of AN, BMI, fat-free mass, and PYY to BMD. For PA and lateral spine, PYY was the primary determinant of BMD, accounting for 59% and 67% of the variability, respectively. Fat-free mass and duration of anorexia nervosa were the primary determinants of BMD at other skeletal sites.
Conclusions: In women with anorexia nervosa, an elevated PYY level is strongly associated with diminished BMD, particularly at the spine. Therefore further investigation of the hypothesis that PYY may contribute to the prevalent bone pathology in this disorder is merited.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Estrogen and peptide YY are associated with bone mineral density in premenopausal exercising women.Bone. 2011 Aug;49(2):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.04.011. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Bone. 2011. PMID: 21549231
-
Relationships between serum adipokines, insulin levels, and bone density in girls with anorexia nervosa.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jun;92(6):2046-52. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-2855. Epub 2007 Mar 13. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17356044
-
Plasma sodium level is associated with bone loss severity in women with anorexia nervosa: a cross-sectional study.J Clin Psychiatry. 2012 Nov;73(11):e1379-83. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07919. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23218167 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between bone mineral density, body composition and amenorrhoea in females with eating disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Eat Disord. 2022 Nov 18;10(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s40337-022-00694-8. J Eat Disord. 2022. PMID: 36401318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrinology of anorexia nervosa in young people: recent insights.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014 Feb;21(1):64-70. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000026. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014. PMID: 24275621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroendocrine adaptations to starvation.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2023 Nov;157:106365. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2023.106365. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37573628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone health in anorexia nervosa.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011 Dec;18(6):376-82. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e32834b4bdc. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011. PMID: 21897220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low bone mineral density in anorexia nervosa: Treatments and challenges.Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab. 2019 Jun;17(2):65-76. doi: 10.1007/s12018-019-09260-4. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab. 2019. PMID: 31938025 Free PMC article.
-
Anorexia Nervosa and Its Associated Endocrinopathy in Young People.Horm Res Paediatr. 2016;85(3):147-57. doi: 10.1159/000443735. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Horm Res Paediatr. 2016. PMID: 26863308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The endocrine manifestations of anorexia nervosa: mechanisms and management.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Mar;13(3):174-186. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.175. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27811940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ducy P, Amling M, Takeda S, Priemel M, Schilling AF, Beil FT, Shen J, Vinson C, Rueger JM, Karsenty G. Leptin inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: a central control of bone mass. Cell. 2000;100:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Takeda S, Elefteriou F, Levasseur R, Liu X, Zhao L, Parker KL, Armstrong D, Ducy P, Karsenty G. Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell. 2002;111:305–317. - PubMed
-
- Elefteriou F, Takeda S, Ebihara K, Magre J, Patano N, Ae Kim C, Ogawa Y, Liu X, Ware SM, Craigen WJ, Robert JJ, Vinson C, Nakao K, Capeau J, Karsenty G. Serum leptin level is a regulator of bone mass. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:3258–3263. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

