A genomic analysis of RNA polymerase II modification and chromatin architecture related to 3' end RNA polyadenylation
- PMID: 18487515
- PMCID: PMC2493437
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.075804.107
A genomic analysis of RNA polymerase II modification and chromatin architecture related to 3' end RNA polyadenylation
Abstract
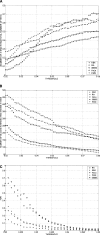
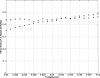
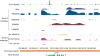
Genomic analyses have been applied extensively to analyze the process of transcription initiation in mammalian cells, but less to transcript 3' end formation and transcription termination. We used a novel approach to prepare 3' end fragments from polyadenylated RNA, and mapped the position of the poly(A) addition site using oligonucleotide arrays tiling 1% of the human genome. This approach revealed more 3' ends than had been annotated. The distribution of these ends relative to RNA polymerase II (PolII) and di- and trimethylated lysine 4 and lysine 36 of histone H3 was compared. A substantial fraction of unannotated 3' ends of RNA are intronic and antisense to the embedding gene. Poly(A) ends of annotated messages lie on average 2 kb upstream of the end of PolII binding (termination). Near the termination sites, and in some internal sites, unphosphorylated and C-terminal domain (CTD) serine 2 phosphorylated PolII (POLR2A) accumulate, suggesting pausing of the polymerase and perhaps dephosphorylation prior to release. Lysine 36 trimethylation occurs across transcribed genes, sometimes alternating with stretches of DNA in which lysine 36 dimethylation is more prominent. Lysine 36 methylation decreases at or near the site of polyadenylation, sometimes disappearing before disappearance of phosphorylated RNA PolII or release of PolII from DNA. Our results suggest that transcription termination loss of histone 3 lysine 36 methylation and later release of RNA polymerase. The latter is often associated with polymerase pausing. Overall, our study reveals extensive sites of poly(A) addition and provides insights into the events that occur during 3' end formation.
Figures





References
-
- Ahn S.H., Kim M., Buratowski S., Kim M., Buratowski S., Buratowski S. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol. Cell. 2004;13:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Barski A., Cuddapah S., Cui K., Roh T.Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Cuddapah S., Cui K., Roh T.Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Cui K., Roh T.Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Roh T.Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Chepelev I., Zhao K., Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Beaudoing E., Freier S., Wyatt J.R., Claverie J.M., Gautheret D., Freier S., Wyatt J.R., Claverie J.M., Gautheret D., Wyatt J.R., Claverie J.M., Gautheret D., Claverie J.M., Gautheret D., Gautheret D. Patterns of variant polyadenylation signal usage in human genes. Genome Res. 2000;10:1001–1010. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernstein B.E., Kamal M., Lindblad-Toh K., Bekiranov S., Bailey D.K., Huebert D.J., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Kamal M., Lindblad-Toh K., Bekiranov S., Bailey D.K., Huebert D.J., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Lindblad-Toh K., Bekiranov S., Bailey D.K., Huebert D.J., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Bekiranov S., Bailey D.K., Huebert D.J., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Bailey D.K., Huebert D.J., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Huebert D.J., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., McMahon S., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Karlsson E.K., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Kulbokas E.J., Gingeras T.R., Gingeras T.R., et al. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell. 2005;120:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Bertone P., Stolc V., Royce T.E., Rozowsky J.S., Urban A.E., Zhu X., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Stolc V., Royce T.E., Rozowsky J.S., Urban A.E., Zhu X., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Royce T.E., Rozowsky J.S., Urban A.E., Zhu X., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Rozowsky J.S., Urban A.E., Zhu X., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Urban A.E., Zhu X., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Zhu X., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Rinn J.L., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Tongprasit W., Samanta M., Weissman S., Samanta M., Weissman S., Weissman S., et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
