Beta-1,3:1,4-glucan synthase activity in rice seedlings under water
- PMID: 18487614
- PMCID: PMC2712359
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcn077
Beta-1,3:1,4-glucan synthase activity in rice seedlings under water
Abstract
Background and aims: The metabolism of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan regulates the mechanical properties of cell walls, and thereby changes the elongation growth of Poaceae plants. A previous study has shown that elongation growth of rice coleoptiles under water is enhanced by increased activity of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan hydrolases; however, the involvement of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase activity in elongation growth under water has not yet been clarified.
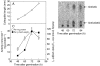
Methods: The beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase activity in a microsomal fraction prepared from rice seedlings grown under water was compared with that from control seedlings grown in air. The change under water in the relative expression level of CslF6, a major isoform of the beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase genes, was examined by quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR.
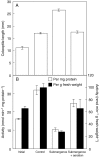
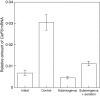
Key results: The level of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase activity in submerged seedlings decreased to less than 40 % of that of the control seedlings and was accompanied by a significant reduction in the amount of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan in the cell walls. Under water, the expression of CslF6 was reduced to less than 20 % of the unsubmerged control. Bubble aeration partially restored both beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase activity and the expression of CslF6 under water, correlating with suppression of the submergence-induced elongation growth of coleoptiles.
Conclusions: Submergence down-regulates the expression of the CslF6 gene, leading to a decreased level of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase activity. Together with the increased activity of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan hydrolases, the decreased activity of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthase contributes to the decrease in the amount of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan in the cell walls under water. The suppression of beta-1,3 : 1,4-glucan synthesis under water may be mainly due to oxygen depletion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of Cellulose synthase-like F6 function affects mixed-linkage glucan deposition, cell wall mechanical properties, and defense responses in vegetative tissues of rice.Plant Physiol. 2012 May;159(1):56-69. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.195495. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22388489 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of the CSLF6 gene results in decreased (1,3;1,4)-beta-D-glucan in endosperm of wheat.Plant Physiol. 2010 Mar;152(3):1209-18. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.151712. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20089768 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the primary cell walls of seedlings of Brachypodium distachyon--a potential model plant for temperate grasses.Phytochemistry. 2010 Jan;71(1):62-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.09.019. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Phytochemistry. 2010. PMID: 19828160
-
Over-expression of specific HvCslF cellulose synthase-like genes in transgenic barley increases the levels of cell wall (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucans and alters their fine structure.Plant Biotechnol J. 2011 Feb;9(2):117-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00532.x. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011. PMID: 20497371
-
Quantifying ATP turnover in anoxic coleoptiles of rice (Oryza sativa) demonstrates preferential allocation of energy to protein synthesis.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jul;63(12):4389-402. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers114. Epub 2012 May 13. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22585748 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of β-d-glucan biosynthetic genes in oat reveals glucan synthesis regulation by light.Ann Bot. 2021 Feb 9;127(3):371-380. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcaa185. Ann Bot. 2021. PMID: 33090200 Free PMC article.
-
Action of an endo-β-1,3(4)-glucanase on cellobiosyl unit structure in barley β-1,3:1,4-glucan.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(11):1810-7. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1046365. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26027730 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the subcellular location of synthesis and assembly of the cell wall polysaccharide (1,3; 1,4)-β-D-glucan in grasses.Plant Cell. 2015 Mar;27(3):754-71. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.135970. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Plant Cell. 2015. PMID: 25770111 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation and synthesis of β-glucans by a Magnaporthe oryzae endotransglucosylase, a member of the glycoside hydrolase 7 family.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13821-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.448902. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23530038 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Cellulose synthase-like F6 function affects mixed-linkage glucan deposition, cell wall mechanical properties, and defense responses in vegetative tissues of rice.Plant Physiol. 2012 May;159(1):56-69. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.195495. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22388489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker M, Vincent C, Reid JS. Biosynthesis of (1,3)(1,4)-β-glucan and (1,3)-β-glucan in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Properties of the membrane-bound glucan synthases. Planta. 1995;95:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Burton RA, Wilson SM, Hrmova M, Harvey AJ, Shirley NJ, Medhurst A, et al. Cellulose synthase-like CslF genes mediate the synthesis of cell wall (1,3;1,4)-β-D-glucans. Science. 2006;311:1940–1942. - PubMed
-
- Carpita NC, Gibeaut DM. Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. The Plant Journal. 1993;3:1–30. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Kamisaka S, Hoson T. Breakdown of (1 → 3)(1 → 4)-β-D-glucans during development of rice coleoptiles in air and under water. Journal of Plant Physiology. 1999;a 155:234–239.

