Classifying late-onset dementia with MRI: is arteriosclerotic brain degeneration the most common cause of Alzheimer's syndrome?
- PMID: 18488889
- PMCID: PMC2544365
- DOI: 10.2147/cia.s2537
Classifying late-onset dementia with MRI: is arteriosclerotic brain degeneration the most common cause of Alzheimer's syndrome?
Abstract
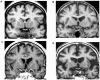
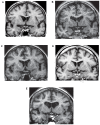
Our aim was to use early magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to investigate the causes of cognitive decline in elderly people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Baseline structural and flow quantification MR sequences, and clinical and neuropsychological follow-up for at least two years, were performed on 62 elderly subjects with MCI. Of these subjects, 17 progressed to dementia, and 15 of these progressed to dementia of the Alzheimer type (DAT). Conversion to clinically diagnosed DAT was related to six distinct MR profiles, including one profile suggesting severe AD (20% of these converters) and five profiles suggesting severe cerebrovascular dysfunction. Two profiles suggested arteriosclerotic brain degeneration, one profile suggested severe venous windkessel dysfunction, and two suggested marked cerebral hypoperfusion associated with very low craniospinal compliance or marked brain atrophy. As compared with vascular MR type converters, AD MR type converters showed high executive and mobility predementia performances. Severe whole anteromesial temporal atrophy and predominantly left brain atrophy on visual MR analysis was only observed in AD MR type converters. In conclusion, these observations enhance the pathogenic complexity of the Alzheimer syndrome, and suggest that the role of arteriosclerotic brain degeneration in late life dementia is underestimated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bateman GA, Levi CR, Schofield P, et al. The pathophysiology of the aqueduct stroke volume in normal pressure hydrocephalus: can co-morbidity with other forms of dementia be excluded? Neuroradiol. 2005;47:741–8. - PubMed
-
- Bateman GA, Levi CR, Schofield P, et al. Quantitative measurements of cerebral haemodynamics in early vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. J ClinNeurosci. 2006;13:563–8. - PubMed
-
- Bateman GA, Loiselle AM. Can MR measurement of intracranial hydrodynamics and compliance differentiate which patient with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus will improve following shunt insertion? Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2007;149:455–62. - PubMed
-
- Baumbach GL. Effects of increased pulse pressure on cerebral arterioles. Hypertension. 1996;27:159–67. - PubMed
-
- Bell-McGinty S, Lopez OL, Cidis-Meltzer C, et al. Differential cortical atrophy in subgroups of mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1393–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

