Intraflagellar transport, cilia, and mammalian Hedgehog signaling: analysis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- PMID: 18488998
- PMCID: PMC2702862
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.21551
Intraflagellar transport, cilia, and mammalian Hedgehog signaling: analysis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Abstract
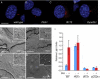
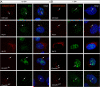
Genetic studies in the mouse have shown that Intraflagellar Transport (IFT) is essential for mammalian Hedgehog (Hh) signal transduction. In this study, we take advantage of wild type and IFT mutant mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) to characterize additional aspects of the relationship between IFT and Hh signaling. Exposure to Sonic hedgehog (Shh) ligand or expression of an activated allele of Smo, SmoA1, activates an Hh reporter in wild-type MEFs, but not in MEFs derived from embryos that lack IFT172 or the Dync2h1 subunit of the retrograde IFT motor. Similarly, decreased activity of either Sufu or PKA, two negative regulators of Hh signal transduction, activates the pathway in wild-type, but not IFT mutant, MEFs. In contrast to wild-type MEFs, Smo is constitutively present in the cilia of Dync2h1 mutant MEFs. This finding suggests that IFT-dependent trafficking of Hh pathway components through the cilium is essential for their function.
Copyright (c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
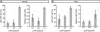
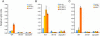
Similar articles
-
Intraflagellar transport protein 122 antagonizes Sonic Hedgehog signaling and controls ciliary localization of pathway components.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1456-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011410108. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21209331 Free PMC article.
-
Cilia and Hedgehog responsiveness in the mouse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 9;102(32):11325-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505328102. Epub 2005 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16061793 Free PMC article.
-
A novel murine allele of Intraflagellar Transport Protein 172 causes a syndrome including VACTERL-like features with hydrocephalus.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Oct 1;20(19):3725-37. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr241. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21653639 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling pathway: a novel model and molecular mechanisms of signal transduction.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(7):1317-32. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2127-4. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26762301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sonic Hedgehog activates the GTPases Rac1 and RhoA in a Gli-independent manner through coupling of smoothened to Gi proteins.Sci Signal. 2011 Nov 22;4(200):pt7. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002396. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 22114142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Hedgehog signal transduction network.Sci Signal. 2012 Oct 16;5(246):re6. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002906. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 23074268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubule Motors Drive Hedgehog Signaling in Primary Cilia.Trends Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;27(2):110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27765513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sporadic hypothalamic hamartoma is a ciliopathy with somatic and bi-allelic contributions.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Jul 21;31(14):2307-2316. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab366. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 35137044 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between TULP3 tubby domain and ARL13B amphipathic helix promote lipidated protein transport to cilia.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Mar 1;34(3):ar18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-10-0473. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36652335 Free PMC article.
-
A crucial role for primary cilia in cortical morphogenesis.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 26;28(48):12887-900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2084-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19036983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey EC, Milenkovic L, Scott MP, Collawn JF, Johnson RL. Several PATCHED1 missense mutations display activity in patched1-deficient fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:33632–33640. - PubMed
-
- Barnfield PC, Zhang X, Thanabalasingham V, Yoshida M, Hui CC. Negative regulation of Gli1 and Gli2 activator function by Suppressor of fused through multiple mechanisms. Differentiation. 2005;73:397–405. - PubMed
-
- Clegg CH, Correll LA, Cadd GG, McKnight GS. Inhibition of intracellular cAMP-dependent protein kinase using mutant genes of the regulatory type I subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:13111–13119. - PubMed
-
- Cooper AF, Yu KP, Brueckner M, Brailey LL, Johnson L, McGrath JM, Bale AE. Cardiac and CNS defects in a mouse with targeted disruption of suppressor of fused. Development. 2005;132:4407–4417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

