Mechanisms of pulsed laser microbeam release of SU-8 polymer "micropallets" for the collection and separation of adherent cells
- PMID: 18489124
- PMCID: PMC2525502
- DOI: 10.1021/ac800129a
Mechanisms of pulsed laser microbeam release of SU-8 polymer "micropallets" for the collection and separation of adherent cells
Abstract
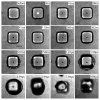
The release of individual polymer micropallets from glass substrates using highly focused laser pulses has been demonstrated for the efficient separation, collection, and expansion of single, adherent cells from a heterogeneous cell population. Here, we use fast-frame photography to examine the mechanism and dynamics of micropallet release produced by pulsed laser microbeam irradiation at lambda = 532 nm using pulse durations ranging between 240 ps and 6 ns. The time-resolved images show the laser microbeam irradiation to result in plasma formation at the interface between the glass coverslip and the polymer micropallet. The plasma formation results in the emission of a shock wave and the ablation of material within the focal volume. Ablation products are generated at high pressure due to the confinement offered by the polymer adhesion to the glass substrate. The ablation products expand underneath the micropallet on a time scale of several hundred nanoseconds. This expansion disrupts the polymer-glass interface and accomplishes the release of the pallet from its glass substrate on the microsecond time scale (approximately 1.5 micros). Our experimental investigation demonstrates that the threshold energy for pallet release is constant (approximately 2 microJ) over a 25-fold range of pulse duration spanning the picosecond to nanosecond domain. Taken together, these results implicate that pallet release accomplished via pulsed laser microbeam irradiation is an energy-driven plasma-mediated ablation process.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Impact of release dynamics of laser-irradiated polymer micropallets on the viability of selected adherent cells.J R Soc Interface. 2012 Jun 7;9(71):1156-67. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2011.0691. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J R Soc Interface. 2012. PMID: 22158840 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrodynamic determinants of cell necrosis and molecular delivery produced by pulsed laser microbeam irradiation of adherent cells.Biophys J. 2013 Nov 5;105(9):2221-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.09.027. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 24209868 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the laser-based release of micropallets from arrays.J Biomed Opt. 2008 May-Jun;13(3):034007. doi: 10.1117/1.2937475. J Biomed Opt. 2008. PMID: 18601552 Free PMC article.
-
Use of near infrared femtosecond lasers as sub-micron radiation microbeam for cell DNA damage and repair studies.Mutat Res. 2010 Apr-Jun;704(1-3):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2010.01.003. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20079460 Review.
-
Application of femtosecond-laser induced nanostructures in optical memory.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2007 Jan;7(1):94-104. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17455477 Review.
Cited by
-
Micropatterned photodegradable hydrogels for the sorting of microbeads and cells.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Aug 26;52(35):9224-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201303965. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 23868693 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ultrasound-induced release of micropallets with cells.Appl Phys Lett. 2012 Oct 15;101(16):163703. doi: 10.1063/1.4757648. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Appl Phys Lett. 2012. PMID: 23152640 Free PMC article.
-
Microtable arrays for culture and isolation of cell colonies.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Nov;398(6):2595-604. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3984-1. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20644916 Free PMC article.
-
Contact printing of arrayed microstructures.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Aug;397(8):3377-85. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3728-2. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20425106 Free PMC article.
-
Microcup arrays for the efficient isolation and cloning of cells.Anal Chem. 2010 Apr 15;82(8):3161-7. doi: 10.1021/ac100434v. Anal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20199088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schütze K, Pösl H, Lahr G. Cell Mol Biol. 1998;44(5):735–746. - PubMed
-
- Schütze K, Lahr G. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16(8):737–742. - PubMed
-
- Mayer A, Stich M, Brocksch D, Schütze K, Lahr G. Methods Enzymol. 2002;356:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Stich M, Thalhammer S, Burgemeister R, Friedemann G, Ehnle S, Lüthy C, Schütze K. Pathol Res Pract. 2003;199:405–409. - PubMed
-
- Vogel A, Horneffer V, Lorenz K, Linz N, Hüttmann G, Gebert A. Methods Cell Biol. 2007;82:153–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

