Phosphorylation of threonine 61 by cyclin a/Cdk1 triggers degradation of stem-loop binding protein at the end of S phase
- PMID: 18490441
- PMCID: PMC2447125
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01416-07
Phosphorylation of threonine 61 by cyclin a/Cdk1 triggers degradation of stem-loop binding protein at the end of S phase
Abstract
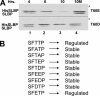
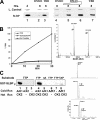
Histone mRNA levels are cell cycle regulated, and a major regulatory mechanism is restriction of stem-loop binding protein (SLBP) to S phase. Degradation of SLBP at the end of S phase results in cessation of histone mRNA biosynthesis, preventing accumulation of histone mRNA until SLBP is synthesized just before entry into the next S phase. Degradation of SLBP requires an SFTTP (58 to 62) and KRKL (95 to 98) sequence, which is a putative cyclin binding site. A fusion protein with the 58-amino-acid sequence of SLBP (amino acids 51 to 108) fused to glutathione S-transferase (GST) is sufficient to mimic SLBP degradation at late S phase. Using GST-SLBP fusion proteins as a substrate, we show that cyclin A/Cdk1 phosphorylates Thr61. Furthermore, knockdown of Cdk1 by RNA interference stabilizes SLBP at the end of S phase. Phosphorylation of Thr61 is necessary for subsequent phosphorylation of Thr60 by CK2 in vitro. Inhibitors of CK2 also prevent degradation of SLBP at the end of S phase. Thus, phosphorylation of Thr61 by cyclin A/Cdk1 primes phosphorylation of Thr60 by CK2 and is responsible for initiating SLBP degradation. We conclude that the increase in cyclin A/Cdk1 activity at the end of S phase triggers degradation of SLBP at S/G(2).
Figures







References
-
- Archambault, V., N. E. Buchler, G. M. Wilmes, M. D. Jacobson, and F. R. Cross. 2005. Two-faced cyclins with eyes on the targets. Cell Cycle 4125-130. - PubMed
-
- Baldin, V., C. Cans, M. Knibiehler, and B. Ducommun. 1997. Phosphorylation of human CDC25B phosphatase by CDK1-cyclin A triggers its proteasome-dependent degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 27232731-32734. - PubMed
-
- Brown, N. R., M. E. Noble, J. A. Endicott, and L. N. Johnson. 1999. The structural basis for specificity of substrate and recruitment peptides for cyclin-dependent kinases. Nat. Cell Biol. 1438-443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
