Neutrophil secretion products pave the way for inflammatory monocytes
- PMID: 18490516
- PMCID: PMC3400540
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-139634
Neutrophil secretion products pave the way for inflammatory monocytes
Abstract
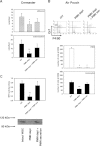
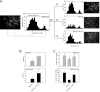
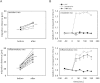
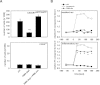
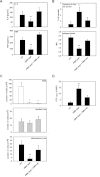
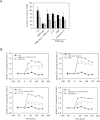
The leukocyte response in inflammation is characterized by an initial recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) preceding a second wave of monocytes to the site of injury or infection. In the mouse, 2 populations of monocytes have been identified, Gr1(-)CCR2(-)CX3CR1(hi) resident monocytes and Gr1(+)CCR2(+)CX3CR1(lo) inflammatory monocytes. Here, intravital microscopy of the musculus cremaster and a subcutaneous air pouch model were used to investigate a possible link between PMN extravasation and the subsequent emigration of inflammatory monocytes in response to local stimulation with PAF. In mice that were made neutropenic by injection of a PMN-depleting antibody, the extravasation of inflammatory monocytes, but not resident monocytes, was markedly reduced compared with mice with intact white blood cell count but was restored by local treatment with secretion of activated PMN. Components of the PMN secretion were found to directly activate inflammatory monocytes and further examination revealed PMN-derived LL-37 and heparin-binding protein (HBP/CAP37/azurocidin) as primary mediators of the recruitment of inflammatory monocytes via activation of formyl-peptide receptors. These data show that LL-37 and HBP specifically stimulate mobilization of inflammatory monocytes. This cellular cross-talk functionally results in enhanced cytokine levels and increased bacterial clearance, thus boosting the early immune response.
Figures

References
-
- Witko-Sarsat V, Rieu P, Descamps-Latscha B, Lesavre P, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L. Neutrophils: molecules, functions and pathophysiological aspects. Lab Invest. 2000;80:617–653. - PubMed
-
- Doherty DE, Downey GP, Worthen GS, Haslett C, Henson PM. Monocyte retention and migration in pulmonary inflammation. Requirement for neutrophils. Lab Invest. 1988;59:200–213. - PubMed
-
- Janardhan KS, Sandhu SK, Singh B. Neutrophil depletion inhibits early and late monocyte/macrophage increase in lung inflammation. Front Biosci. 2006;11:1569–1576. - PubMed
-
- Fillion I, Ouellet N, Simard M, et al. Role of chemokines and formyl peptides in pneumococcal pneumonia-induced monocyte/macrophage recruitment. J Immunol. 2001;166:7353–7361. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Stohlman SA, Hinton DR, Marten NW. Neutrophils promote mononuclear cell infiltration during viral-induced encephalitis. J Immunol. 2003;170:3331–3336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

