Luteolin reduces IL-6 production in microglia by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation and activation of AP-1
- PMID: 18490655
- PMCID: PMC2396685
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0802865105
Luteolin reduces IL-6 production in microglia by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation and activation of AP-1
Abstract
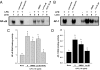
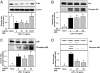
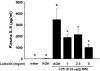
Luteolin, a flavonoid found in high concentrations in celery and green pepper, has been shown to reduce production of proinflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated macrophages, fibroblasts, and intestinal epithelial cells. Because excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines by activated brain microglia can cause behavioral pathology and neurodegeneration, we sought to determine whether luteolin also regulates microglial cell production of a prototypic inflammatory cytokine, IL-6. Pretreatment of primary murine microlgia and BV-2 microglial cells with luteolin inhibited LPS-stimulated IL-6 production at both the mRNA and protein levels. To determine how luteolin inhibited IL-6 production in microglia, EMSAs were performed to establish the effects of luteolin on LPS-induced binding of transcription factors to the NF-kappaB and activator protein-1 (AP-1) sites on the IL-6 promoter. Whereas luteolin had no effect on the LPS-induced increase in NF-kappaB DNA binding activity, it markedly reduced AP-1 transcription factor binding activity. Consistent with this finding, luteolin did not inhibit LPS-induced degradation of IkappaB-alpha but inhibited JNK phosphorylation. To determine whether luteolin might have similar effects in vivo, mice were provided drinking water supplemented with luteolin for 21 days and then they were injected i.p. with LPS. Luteolin consumption reduced LPS-induced IL-6 in plasma 4 h after injection. Furthermore, luteolin decreased the induction of IL-6 mRNA by LPS in hippocampus but not in the cortex or cerebellum. Taken together, these data suggest luteolin inhibits LPS-induced IL-6 production in the brain by inhibiting the JNK signaling pathway and activation of AP-1 in microglia. Thus, luteolin may be useful for mitigating neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
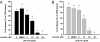
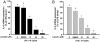
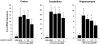
References
-
- Laflamme N, Rivest S. Toll-like receptor 4: The missing link of the cerebral innate immune response triggered by circulating gram-negative bacterial cell wall components. FASEB J. 2001;15:155–163. - PubMed
-
- Guha M, Mackman N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 2001;13:85–94. - PubMed
-
- Godbout JP, et al. Exaggerated neuroinflammation and sickness behavior in aged mice following activation of the peripheral innate immune system. FASEB J. 2005;19:1329–1331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

