B cell survival: an unexpected mechanism of lymphocyte vitality
- PMID: 18490932
- PMCID: PMC3821797
- DOI: 10.1038/icb.2008.35
B cell survival: an unexpected mechanism of lymphocyte vitality
Figures
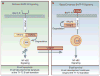
References
-
- Gardam S, Sierro F, Basten A, Mackay F, Brink R. TRAF2 and TRAF3 signal adapters act cooperatively to control the maturation and survival signals delivered to B cells by the BAFF receptor. Immunity. 2008;28:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Mackay F, Schneider P, Rennert P, Browning J. BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B cell survival. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:231–264. - PubMed
-
- Schiemann B, Gommerman JL, Vora K, Cachero TG, Shulga-Morskaya S, Dobles M, et al. An essential role for BAFF in the normal development of B cells through a BCMA-independent pathway. Science. 2001;293:2111–2114. - PubMed
-
- Gross JA, Dillon SR, Mudri S, Johnston J, Littau A, Roque R, et al. TACI-Ig neutralizes molecules critical for B cell development and autoimmune disease. Impaired B cell maturation in mice lacking BLyS. Immunity. 2001;15:289–302. - PubMed
-
- Thompson JS, Bixler SA, Qian F, Vora K, Scott ML, Cachero TG, et al. BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically interacts with BAFF. Science. 2001;293:2108–2111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

