Anaplastic oligodendrogliomas with 1p19q codeletion have a proneural gene expression profile
- PMID: 18492260
- PMCID: PMC2415112
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-41
Anaplastic oligodendrogliomas with 1p19q codeletion have a proneural gene expression profile
Abstract
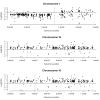
Background: In high grade gliomas, 1p19q codeletion and EGFR amplification are mutually exclusive and predictive of dramatically different outcomes. We performed a microarray gene expression study of four high grade gliomas with 1p19q codeletion and nine with EGFR amplification, identified by CGH-array.
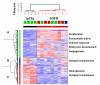
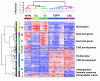
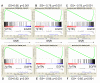
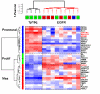
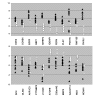
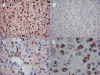
Results: The two groups of gliomas exhibited very different gene expression profiles and were consistently distinguished by unsupervised clustering analysis. One of the most striking differences was the expression of normal brain genes by oligodendrogliomas with 1p19q codeletion. These gliomas harbored a gene expression profile that partially resembled the gene expression of normal brain samples, whereas gliomas with EGFR amplification expressed many genes in common with glioblastoma cancer stem cells. The differences between the two types of gliomas and the expression of neuronal genes in gliomas with 1p19q codeletion were both validated in an independent series of 16 gliomas using real-time RT-PCR with a set of 22 genes differentiating the two groups of gliomas (AKR1C3, ATOH8, BMP2, C20orf42, CCNB1, CDK2, CHI3L1, CTTNBP2, DCX, EGFR, GALNT13, GBP1, IGFBP2, IQGAP1, L1CAM, NCAM1, NOG, OLIG2, PDPN, PLAT, POSTN, RNF135). Immunohistochemical study of the most differentially expressed neuronal gene, alpha-internexin, clearly differentiated the two groups of gliomas, with 1p19q codeletion gliomas showing specific staining in tumor cells.
Conclusion: These findings provide evidence for neuronal differentiation in oligodendrogliomas with 1p19q codeletion and support the hypothesis that the cell of origin for gliomas with 1p19q codeletion could be a bi-potential progenitor cell, able to give rise to both neurons and oligodendrocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Jenkins RB, Blair H, Ballman KV, Giannini C, Arusell RM, Law M, Flynn H, Passe S, Felten S, Brown PD, Shaw EG, Buckner JC. A t(1;19)(q10;p10) mediates the combined deletions of 1p and 19q and predicts a better prognosis of patients with oligodendroglioma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9852–9861. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1796. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Idbaih A, Marie Y, Lucchesi C, Pierron G, Manie E, Raynal V, Mosseri V, Hoang-Xuan K, Kujas M, Brito I, Mokhtari K, Sanson M, Barillot E, Aurias A, Delattre JY, Delattre O. BAC array CGH distinguishes mutually exclusive alterations that define clinicogenetic subtypes of gliomas. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:1778–1786. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23270. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dehais C, Laigle-Donadey F, Marie Y, Kujas M, Lejeune J, Benouaich-Amiel A, Pedretti M, Polivka M, Xuan KH, Thillet J, Delattre JY, Sanson M. Prognostic stratification of patients with anaplastic gliomas according to genetic profile. Cancer. 2006;107:1891–1897. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, Williams PM, Modrusan Z, Feuerstein BG, Aldape K. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:157–173. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.02.019. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

