Microbial production of plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
- PMID: 18492807
- PMCID: PMC2396723
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0802981105
Microbial production of plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
Abstract
Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, such as the analgesic compounds morphine and codeine, and the antibacterial agents berberine, palmatine, and magnoflorine, are synthesized from tyrosine in the Papaveraceae, Berberidaceae, Ranunculaceae, Magnoliaceae, and many other plant families. It is difficult to produce alkaloids on a large scale under the strict control of secondary metabolism in plants, and they are too complex for cost-effective chemical synthesis. By using a system that combines microbial and plant enzymes to produce desired benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, we synthesized (S)-reticuline, the key intermediate in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis, from dopamine by crude enzymes from transgenic Escherichia coli. The final yield of (S)-reticuline was 55 mg/liter within 1 h. Furthermore, we synthesized an aporphine alkaloid, magnoflorine, or a protoberberine alkaloid, scoulerine, from dopamine via reticuline by using different combination cultures of transgenic E. coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. The final yields of magnoflorine and scoulerine were 7.2 and 8.3 mg/liter culture medium. These results indicate that microbial systems that incorporate plant genes cannot only enable the mass production of scarce benzylisoquinoline alkaloids but may also open up pathways for the production of novel benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
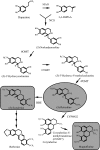


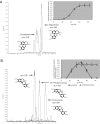
Comment in
-
Production platforms for the molecular pharming of alkaloid diversity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 10;105(23):7897-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803930105. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18541922 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Allen RS, et al. RNAi-mediated replacement of morphine with the nonnarcotic alkaloid reticuline in opium poppy. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:1559–1566. - PubMed
-
- Hung TM, et al. Magnoflorine from Coptidis rhizoma protects high density lipoprotein during oxidant stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30:1157–1160. - PubMed
-
- Hung TM, et al. Protective effect of magnoflorine isolated from Coptidis rhizoma on Cu2+-induced oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. Planta Med. 2007;73:1281–1284. - PubMed
-
- Rashid MA, et al. Anti-HIV alkaloids from Toddalia asiatica. Nat Prod Res. 1995;6:153–156.
-
- Kong W, et al. Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins. Nat Med. 2004;10:1344–1351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

