Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 18492871
- PMCID: PMC2438454
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.058180
Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
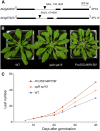
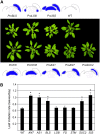
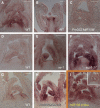
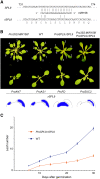
Leaves of flowering plants are produced from the shoot apical meristem at regular intervals, with the time that elapses between the formation of two successive leaf primordia defining the plastochron. We have identified two genetic axes affecting plastochron length in Arabidopsis thaliana. One involves microRNA156 (miR156), which targets a series of SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) genes. In situ hybridization studies and misexpression experiments demonstrate that miR156 is a quantitative, rather than spatial, modulator of SPL expression in leaf primordia and that SPL activity nonautonomously inhibits initiation of new leaves at the shoot apical meristem. The second axis is exemplified by a redundantly acting pair of cytochrome P450 genes, CYP78A5/KLUH and CYP78A7, which are likely orthologs of PLASTOCHRON1 of rice (Oryza sativa). Inactivation of CYP78A5, which is expressed at the periphery of the shoot apical meristem, accelerates the leaf initiation rate, whereas cyp78a5 cyp78a7 double mutants often die as embryos with supernumerary cotyledon primordia. The effects of both miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5 on organ size are correlated with changes in plastochron length, suggesting a potential compensatory mechanism that links the rate at which leaves are produced to final leaf size.
Figures

References
-
- Abe, M., Kobayashi, Y., Yamamoto, S., Daimon, Y., Yamaguchi, A., Ikeda, Y., Ichinoki, H., Notaguchi, M., Goto, K., and Araki, T. (2005). FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309 1052–1056. - PubMed
-
- Adenot, X., Elmayan, T., Lauressergues, D., Boutet, S., Bouche, N., Gasciolli, V., and Vaucheret, H. (2006). DRB4-dependent TAS3 trans-acting siRNAs control leaf morphology through AGO7. Curr. Biol. 16 927–932. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Anastasiou, E., Kenz, S., Gerstung, M., MacLean, D., Timmer, J., Fleck, C., and Lenhard, M. (2007). Control of plant organ size by KLUH/CYP78A5-dependent intercellular signaling. Dev. Cell 13 843–856. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, G.H., Alvarez, N.D.G., Gilman, C., Jeffares, D.C., Trainor, V.C.W., Hanson, M.R., and Veit, B. (2004). Diversification of genes encoding Mei2-Like RNA binding proteins in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 54 653–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

