Clinical application of 1,5-anhydroglucitol measurements in patients with hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- PMID: 18492944
- PMCID: PMC2494661
- DOI: 10.2337/dc07-2334
Clinical application of 1,5-anhydroglucitol measurements in patients with hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha maturity-onset diabetes of the young
Abstract
Objective: 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) is a short-term marker of metabolic control in diabetes. Its renal loss is stimulated in hyperglycemic conditions by glycosuria, which results in a lowered plasma concentration. As a low renal threshold for glucose has been described in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha (HNF-1alpha) maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), the 1,5-AG level may be altered in these patients. The purpose of this study was to assess the 1,5-AG levels in patients with HNF-1alpha MODY and in type 2 diabetic subjects with a similar degree of metabolic control. In addition, we aimed to evaluate this particle as a biomarker for HNF-1alpha MODY.
Research design and methods: We included 33 diabetic patients from the Polish Nationwide Registry of MODY. In addition, we examined 43 type 2 diabetic patients and 47 nondiabetic control subjects. The 1,5-AG concentration was measured with an enzymatic assay (GlycoMark). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate 1,5-AG as a screening marker for HNF-1alpha MODY.
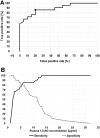
Results: The mean 1,5-AG plasma concentration in diabetic HNF-1alpha mutation carriers was 5.9 microg/ml, and it was lower than that in type 2 diabetic patients (11.0 microg/ml, P = 0.003) and in nondiabetic control subjects (23.9 microg/ml, P < 0.00005). The ROC curve analysis revealed 85.7% sensitivity and 80.0% specificity of 1,5-AG in screening for HNF-1alpha MODY at the criterion of <6.5 microg/ml in patients with an A1C level between 6.5 and 9.0%.
Conclusions: 1,5-AG may be a useful biomarker for differential diagnosis of patients with HNF-1alpha MODY with a specific range of A1C, although this requires further investigation. However, the clinical use of this particle in diabetic HNF-1alpha mutation carriers for metabolic control has substantial limitations.
Figures

References
-
- Yamanouchi T, Tachibana Y, Akanuma H: Origin and disposal of 1,5-anhydroglucitol, a major polyol in the human body. Am J Physiol 263:E268–E273, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Yamanouchi T, Shinohara T, Ogata N, Tachibana Y, Akaoka I, Miyashita H: Common reabsorption system of 1,5-anhydro-d-glucitol, fructose, and mannose in rat renal tubule. Biochim Biophys Acta 1291:89–95, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Saito H, Ohtomo T, Inui K: Na+-dependent uptake of 1,5-anhydro-d-glucitol via the transport systems for d-glucose and d-mannose in the kidney epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 38:435–440, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Stickle D, Turk J: A kinetic mass balance model for 1,5-anhydroglucitol: applications to monitoring of glycemic control. Am J Physiol 273:E821–E830, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Yamanouchi T, Ogata N, Tagaya T, Kawasaki T, Sekino N, Funato H, Akaoka L, Miyashita H: Clinical usefulness of serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol in monitoring glycaemic control. Lancet 347:1514–1518, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

