Functional characterization of the Drosophila Hmt4-20/Suv4-20 histone methyltransferase
- PMID: 18493056
- PMCID: PMC2390611
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.108.087650
Functional characterization of the Drosophila Hmt4-20/Suv4-20 histone methyltransferase
Abstract
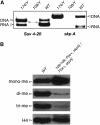
Di- and trimethylation of histone H4 lysine20 (H4K20) are thought to play an important role in controlling gene expression in vertebrates and in Drosophila. By inducing a null mutation in Drosophila Suv4-20, we show that it encodes the histone H4 lysine20 di- and trimethyltransferase. In Suv4-20 mutants, the H4K20 di- and trimethyl marks are strongly reduced or absent, and the monomethyl mark is significantly increased. We find that even with this biochemical function, Suv4-20 is not required for survival and does not control position-effect variegation (PEV).
Figures

References
-
- Cryderman, D. E., M. H. Cuaycong, S. C. Elgin and L. L. Wallrath, 1998. Characterization of sequences associated with position-effect variegation at pericentric sites in Drosophila heterochromatin. Chromosoma 107 277–285. - PubMed
-
- Fang, J., Q. Feng, C. S. Ketel, H. Wang, R. Cao et al., 2002. Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr. Biol. 12 1086–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

