Ubiquitin E3 ligase Ring1b/Rnf2 of polycomb repressive complex 1 contributes to stable maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 18493325
- PMCID: PMC2375055
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002235
Ubiquitin E3 ligase Ring1b/Rnf2 of polycomb repressive complex 1 contributes to stable maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) core member Ring1b/Rnf2, with ubiquitin E3 ligase activity towards histone H2A at lysine 119, is essential for early embryogenesis. To obtain more insight into the role of Ring1b in early development, we studied its function in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells.
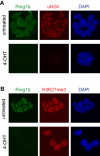
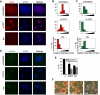
Methodology/principal findings: We investigated the effects of Ring1b ablation on transcriptional regulation using Ring1b conditional knockout ES cells and large-scale gene expression analysis. The absence of Ring1b results in aberrant expression of key developmental genes and deregulation of specific differentiation-related pathways, including TGFbeta signaling, cell cycle regulation and cellular communication. Moreover, ES cell markers, including Zfp42/Rex-1 and Sox2, are downregulated. Importantly, retained expression of ES cell regulators Oct4, Nanog and alkaline phosphatase indicates that Ring1b-deficient ES cells retain important ES cell specific characteristics. Comparative analysis of our expression profiling data with previously published global binding studies shows that the genes that are bound by Ring1b in ES cells have bivalent histone marks, i.e. both active H3K4me3 and repressive H3K27me3, or the active H3K4me3 histone mark alone and are associated with CpG-'rich' promoters. However, deletion of Ring1b results in deregulation, mainly derepression, of only a subset of these genes, suggesting that additional silencing mechanisms are involved in repression of the other Ring1b bound genes in ES cells.
Conclusions: Ring1b is essential to stably maintain an undifferentiated state of mouse ES cells by repressing genes with important roles during differentiation and development. These genes are characterized by high CpG content promoters and bivalent histone marks or the active H3K4me3 histone mark alone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ring1B is crucial for the regulation of developmental control genes and PRC1 proteins but not X inactivation in embryonic cells.J Cell Biol. 2007 Jul 16;178(2):219-29. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200612127. Epub 2007 Jul 9. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17620408 Free PMC article.
-
A phosphorylated form of Mel-18 targets the Ring1B histone H2A ubiquitin ligase to chromatin.Mol Cell. 2007 Oct 12;28(1):107-20. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.08.009. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17936708
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of RING1B is not essential for early mouse development.Genes Dev. 2015 Sep 15;29(18):1897-902. doi: 10.1101/gad.268151.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26385961 Free PMC article.
-
Role of polycomb proteins Ring1A and Ring1B in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression.Int J Dev Biol. 2009;53(2-3):355-70. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082690mv. Int J Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19412891 Review.
-
Bivalent histone modifications in early embryogenesis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;24(3):374-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.03.009. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22513113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Spatiotemporal Expression of Ring1B in the Postnatal Mouse Cochlea.J Int Adv Otol. 2022 Jul;18(4):297-301. doi: 10.5152/iao.2022.21473. J Int Adv Otol. 2022. PMID: 35894525 Free PMC article.
-
F-box protein FBXL16 binds PP2A-B55α and regulates differentiation of embryonic stem cells along the FLK1+ lineage.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Mar;13(3):780-91. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.031765. Epub 2014 Jan 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24390425 Free PMC article.
-
USP26 functions as a negative regulator of cellular reprogramming by stabilising PRC1 complex components.Nat Commun. 2017 Aug 24;8(1):349. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00301-4. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28839133 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic inheritance of cell fates during embryonic development.Front Genet. 2014 Feb 4;5:19. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00019. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24550937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation by Polycomb group proteins.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1147-55. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2669. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24096405 Review.
References
-
- Lund AH, van Lohuizen M. Polycomb complexes and silencing mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Ringrose L, Paro R. Epigenetic regulation of cellular memory by the Polycomb and Trithorax group proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:413–443. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Wang L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Vidal M, Tempst P, et al. Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing. Nature. 2004;431:873–878. - PubMed
-
- Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science. 2002;298:1039–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

