IFN-gamma regulation of vacuolar pH, cathepsin D processing and autophagy in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 18494001
- PMCID: PMC2575810
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.21814
IFN-gamma regulation of vacuolar pH, cathepsin D processing and autophagy in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
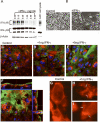
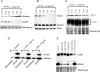
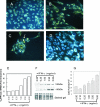
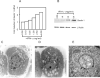
In this study we examined the ability of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) to regulate mammary epithelial cell growth and gene expression, with particular emphasis on two genes: Maspin (a member of serine protease inhibitor superfamily), and the lysosomal aspartyl endopeptidase cathepsin D (CatD). The protein products of these genes are critically involved in regulation of multitude of biological functions in different stages of mammary tissue development and remodeling. In addition, the expression of Maspin is down-regulated in primary breast cancer and is lost in metastatic disease, while CatD is excessively produced and aberrantly secreted by breast cancer cells. We report that IFN-gamma receptors are expressed in mammary epithelial cells, and receptor engagement by IFN-gamma transduces the IFN-gamma signal via Stat-1 resulting in decreased vacuolar pH. This change in vacuolar pH alters CatD protein processing and secretion concurrent with increased Maspin secretion. In addition, IFN-gamma exerts a suppressive effect on cell growth and proliferation, and induces morphological changes in mammary epithelial cells. Our studies also reveal that breast cancer cells, which are devoid of Maspin, are refractory to IFN-gamma with respect to changes in vacuolar pH and CatD. However, Maspin transfection of breast cancer cells partially sensitizes the cells to IFN-gamma's effect, thus providing new therapeutic implications.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

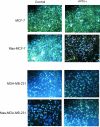
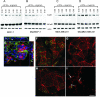
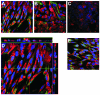
Similar articles
-
New insights into cathepsin D in mammary tissue development and remodeling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Sep 1;10(5):457-66. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.5.12534. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20592493 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the function of secreted maspin: inhibiting cathepsin D-mediated matrix degradation.Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 15;67(8):3535-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4767. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17440060 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy regulator BECN1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis driven by WNT1 activation and following parity.Autophagy. 2014;10(11):2036-52. doi: 10.4161/auto.34398. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 25483966 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
The potential of Beclin 1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of breast cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016;20(2):167-78. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1085971. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26357854 Review.
Cited by
-
Calhex231 ameliorates myocardial fibrosis post myocardial infarction in rats through the autophagy-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in macrophages.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(22):13440-13453. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15969. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33043596 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine interactions between primary human macrophages and human fibroblasts enhance murine mammary gland humanization in vivo.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 25;14(3):R97. doi: 10.1186/bcr3215. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22731827 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into cathepsin D in mammary tissue development and remodeling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Sep 1;10(5):457-66. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.5.12534. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20592493 Free PMC article.
-
Two Faces of Cathepsin D: Physiological Guardian Angel and Pathological Demon.Biol Med (Aligarh). 2014 Jul;6(2):1000206. doi: 10.4172/0974-8369.1000206. Biol Med (Aligarh). 2014. PMID: 25663755 Free PMC article.
-
Immune defenses of the mammary gland epithelium of dairy ruminants.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1031785. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1031785. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey CM, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Kondo S, Margaryan NV, Seftor RE, Wheaton WW, Amir S, Pins MR, Schutte BC, Hendrix MJC. Mammary serine protease inhibitor (Maspin) binds directly to interferon regulatory factor 6: identification of a novel serpin partnership. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:34210–34217. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blacque OE, Worrall DM. Evidence for a direct interaction between the tumor suppressor serpin, maspin, and types I and III collagen. J. Biol.Chem. 2002;277:10783–1078. - PubMed
-
- Braulke T, Geuze HJ, Slot JW, Hasilik A, von Figura K. On the effects of weak bases and monensin on sorting and processing of lysosomal enzymes in human cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1987;43:316–321. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE., Jr. Studies on IFN-induced transcriptional activation uncover Jak-Stat pathway. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998;18:549–5454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

