Endoscopic ultrasound: it's accuracy in evaluating mediastinal lymphadenopathy? A meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 18494054
- PMCID: PMC2712170
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.3028
Endoscopic ultrasound: it's accuracy in evaluating mediastinal lymphadenopathy? A meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), EUS-fine needle aspiration (FNA) in evaluating mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
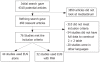
Methods: Only EUS and EUS-FNA studies confirmed by surgery or with appropriate follow-up were selected. Articles were searched in Medline, Pubmed, and Cochrane control trial registry. Only studies from which a 2 multiply 2 table could be constructed for true positive, false negative, false positive and true negative values were included. Two reviewers independently searched and extracted data. The differences were resolved by mutual agreement. Meta-analysis for the accuracy of EUS was analyzed by calculating pooled estimates of sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios, and diagnostic odds ratios. Pooling was conducted by both Mantel-Haenszel method (fixed effects model) and DerSimonian Laird method (random effects model). The heterogeneity of studies was tested using Cochran's Q test based upon inverse variance weights.
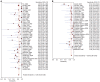
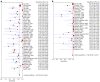
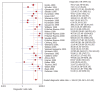
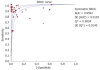
Results: Data was extracted from 76 studies (n = 9310) which met the inclusion criteria. Of these, 44 studies used EUS alone and 32 studies used EUS-FNA. FNA improved the sensitivity of EUS from 84.7% (95% CI: 82.9-86.4) to 88.0% (95% CI: 85.8-90.0). With FNA, the specificity of EUS improved from 84.6% (95% CI: 83.2-85.9) to 96.4% (95% CI: 95.3-97.4). The P for chi-squared heterogeneity for all the pooled accuracy estimates was > 0.10.
Conclusion: EUS is highly sensitive and specific for the evaluation of mediastinal lymphadenopathy and FNA substantially improves this. EUS with FNA should be the diagnostic test of choice for evaluating mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
Figures
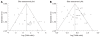
Similar articles
-
How good is endoscopic ultrasound for TNM staging of gastric cancers? A meta-analysis and systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Jul 7;14(25):4011-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4011. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18609685 Free PMC article.
-
Staging accuracy of esophageal cancer by endoscopic ultrasound: a meta-analysis and systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 14;14(10):1479-90. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1479. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18330935 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging modalities for characterising focal pancreatic lesions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 17;4(4):CD010213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010213.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28415140 Free PMC article.
-
Transabdominal ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound for diagnosis of gallbladder polyps.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 15;8(8):CD012233. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012233.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30109701 Free PMC article.
-
Utility and Safety of Endoscopic Ultrasound With Bronchoscope-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration in Mediastinal Lymph Node Sampling: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Respir Care. 2015 Jul;60(7):1040-50. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03779. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Respir Care. 2015. PMID: 25759463
Cited by
-
A quarter century of EUS-FNA: Progress, milestones, and future directions.Endosc Ultrasound. 2018 May-Jun;7(3):141-160. doi: 10.4103/eus.eus_19_18. Endosc Ultrasound. 2018. PMID: 29941723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Era of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition: Next-Generation Sequencing by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Sampling for Pancreatic Cancer.J Clin Med. 2019 Aug 5;8(8):1173. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081173. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31387310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound assessment and tissue acquisition of mediastinal and abdominal lymph nodes.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):1475-1491. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i10.1475. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34721779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interobserver agreement on the endosonographic features of lymph nodes in aerodigestive malignancies.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Nov;56(11):3204-8. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1725-8. Epub 2011 May 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21573731
-
Impact of celiac neurolysis on survival in patients with pancreatic cancer.Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jul;82(1):46-56.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.12.036. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25800661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Genereux GP, Howie JL. Normal mediastinal lymph node size and number: CT and anatomic study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984;142:1095–1100. - PubMed
-
- Izbicki JR, Thetter O, Karg O, Kreusser T, Passlick B, Trupka A, Haussinger K, Woeckel W, Kenn RW, Wilker DK. Accuracy of computed tomographic scan and surgical assessment for staging of bronchial carcinoma. A prospective study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992;104:413–420. - PubMed
-
- McLoud TC, Bourgouin PM, Greenberg RW, Kosiuk JP, Templeton PA, Shepard JA, Moore EH, Wain JC, Mathisen DJ, Grillo HC. Bronchogenic carcinoma: analysis of staging in the mediastinum with CT by correlative lymph node mapping and sampling. Radiology. 1992;182:319–323. - PubMed
-
- McKenna RJ Jr, Libshitz HI, Mountain CE, McMurtrey MJ. Roentgenographic evaluation of mediastinal nodes for preoperative assessment in lung cancer. Chest. 1985;88:206–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

