Dendritic A-type potassium channel subunit expression in CA1 hippocampal interneurons
- PMID: 18495361
- PMCID: PMC2507867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.04.022
Dendritic A-type potassium channel subunit expression in CA1 hippocampal interneurons
Abstract
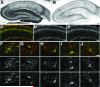
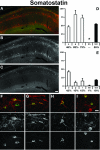
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels are important and diverse determinants of neuronal excitability and exhibit specific expression patterns throughout the brain. Among Kv channels, Kv4 channels are major determinants of somatodendritic A-type current and are essential in controlling the amplitude of backpropagating action potentials (BAPs) into neuronal dendrites. BAPs have been well studied in a variety of neurons, and have been recently described in hippocampal and cortical interneurons, a heterogeneous population of GABAergic inhibitory cells that regulate activity of principal cells and neuronal networks. We used well-characterized mouse monoclonal antibodies against the Kv4.3 and potassium channel interacting protein (KChIP) 1 subunits of A-type Kv channels, and antibodies against different interneuron markers in single- and double-label immunohistochemistry experiments to analyze the expression patterns of Kv4.3 and KChIP1 in hippocampal Ammon's horn (CA1) neurons. Immunohistochemistry was performed on 40 mum rat brain sections using nickel-enhanced diaminobenzidine staining or multiple-label immunofluorescence. Our results show that Kv4.3 and KChIP1 component subunits of A-type channels are co-localized in the soma and dendrites of a large number of GABAergic hippocampal interneurons. These subunits co-localize extensively but not completely with markers defining the four major interneuron subpopulations tested (parvalbumin, calbindin, calretinin, and somatostatin). These results suggest that CA1 hippocampal interneurons can be divided in two groups according to the expression of Kv4.3/KChIP1 channel subunits. Antibodies against Kv4.3 and KChIP1 represent an important new tool for identifying a subpopulation of hippocampal interneurons with a unique dendritic A-type channel complement and ability to control BAPs.
Figures




References
-
- An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Ling HP, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature. 2000;403:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Baimbridge KG, Miller JJ, Parkes CO. Calcium-binding protein distribution in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1982;239:519–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

